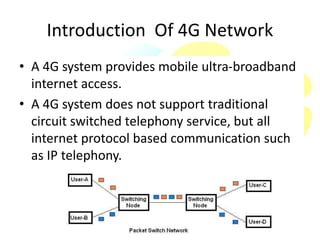
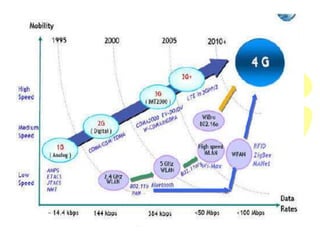
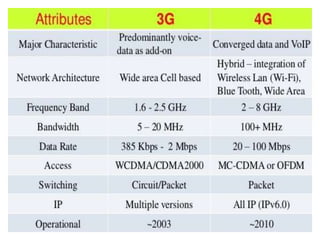
4G wireless networks provide faster internet speeds than 3G networks, aiming to support data rates up to 1 Gbps for high mobility applications and up to 100 Mbps for wide-area coverage applications. 4G networks use an all-IP packet switched network and are optimized for Internet Protocol traffic, allowing services such as video conferencing. Key technologies used in 4G include MIMO antennas, IPv6, VoIP, OFDM, and software-defined radios. While true 4G networks may not be fully realized until after 2015, 4G aims to open new opportunities for mobile applications with high-speed wireless internet access.