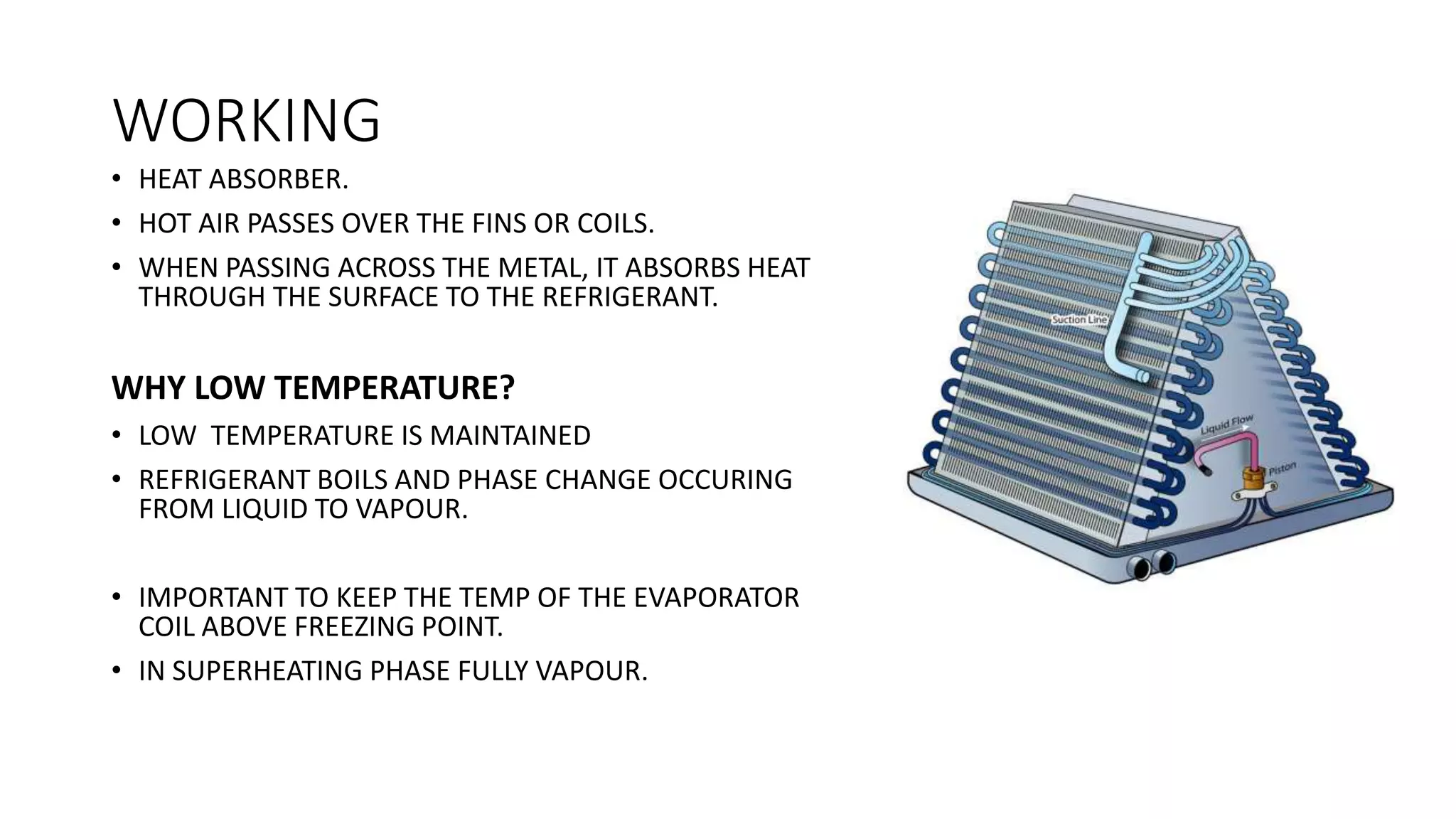
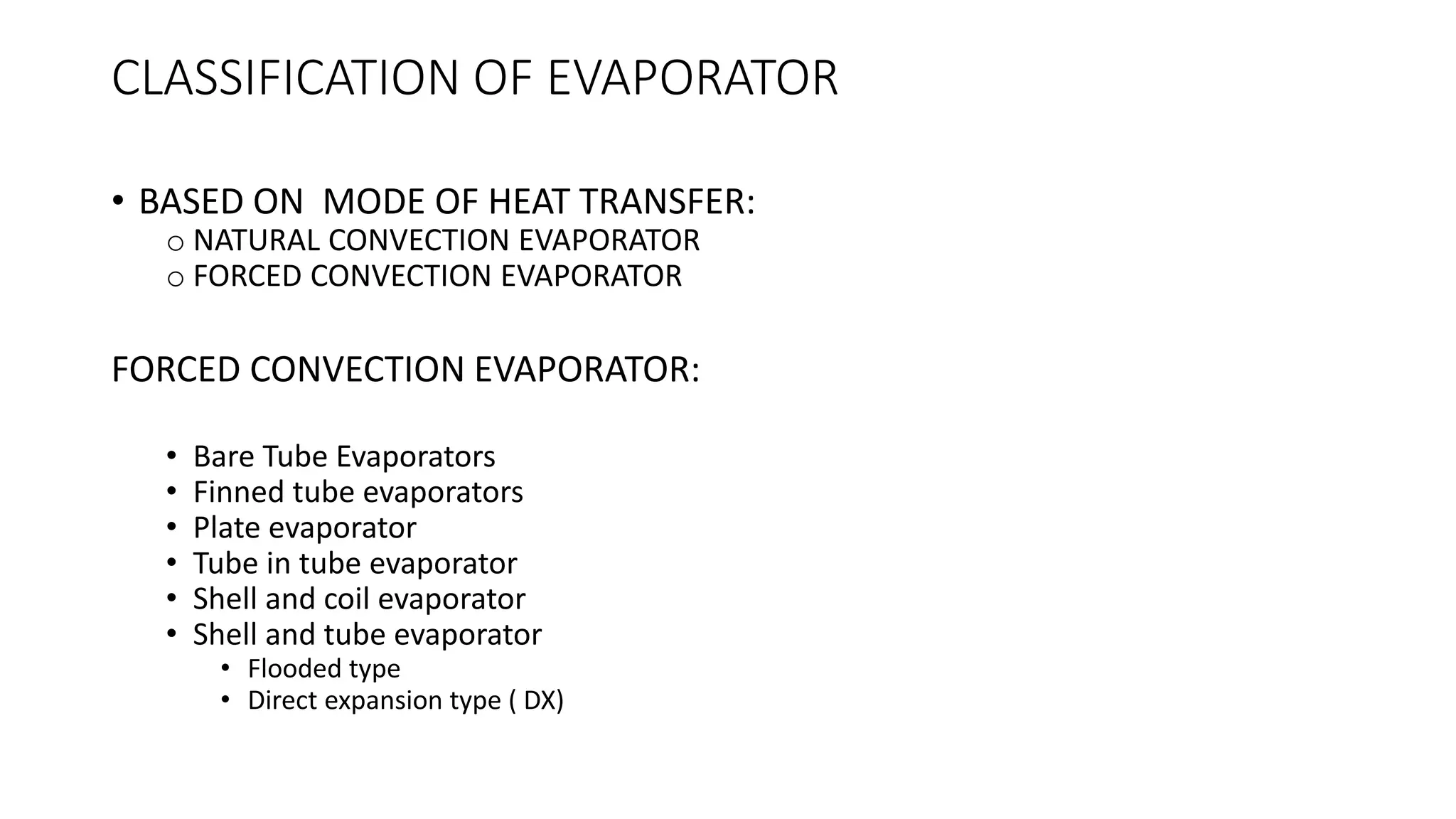
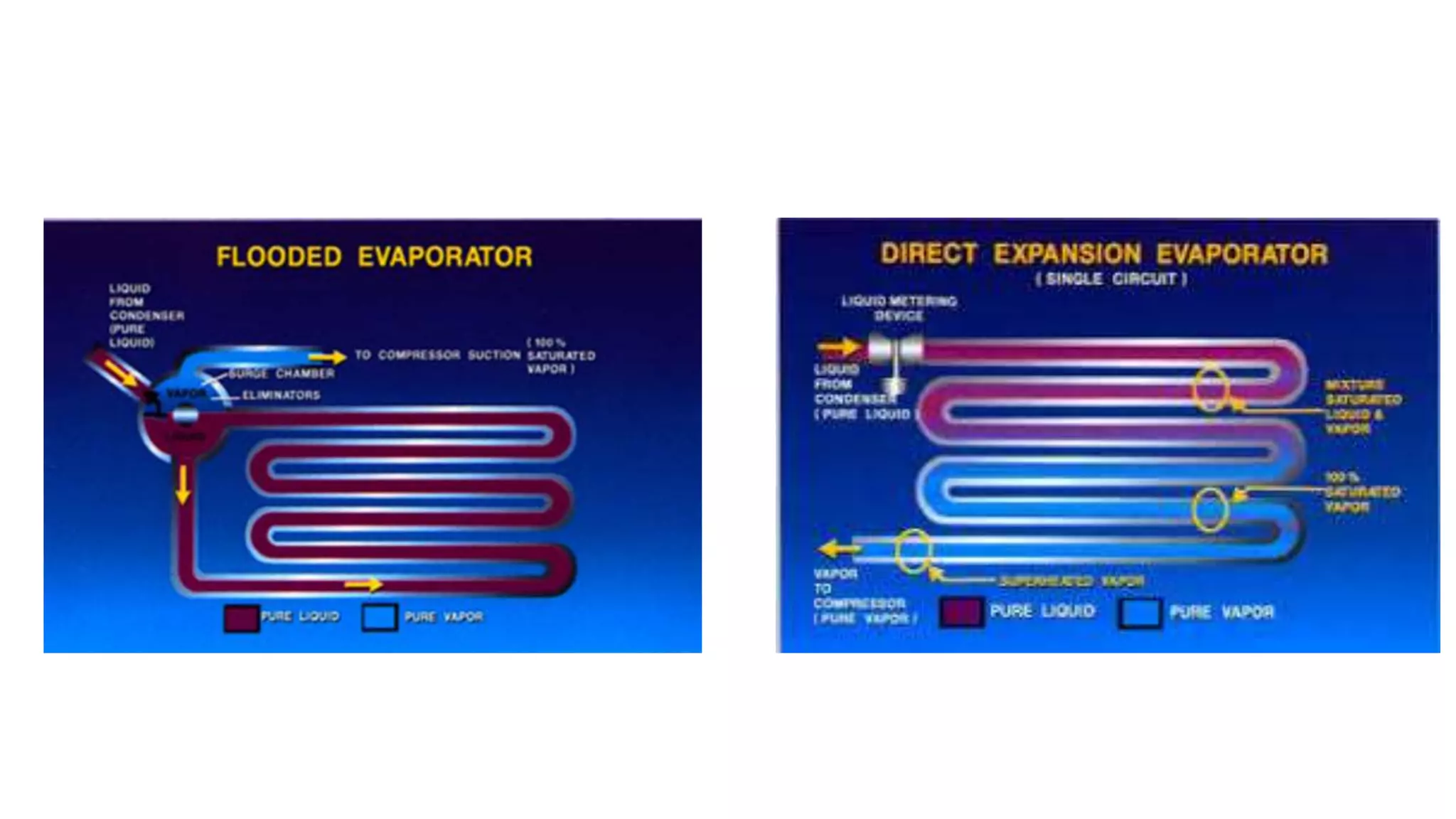
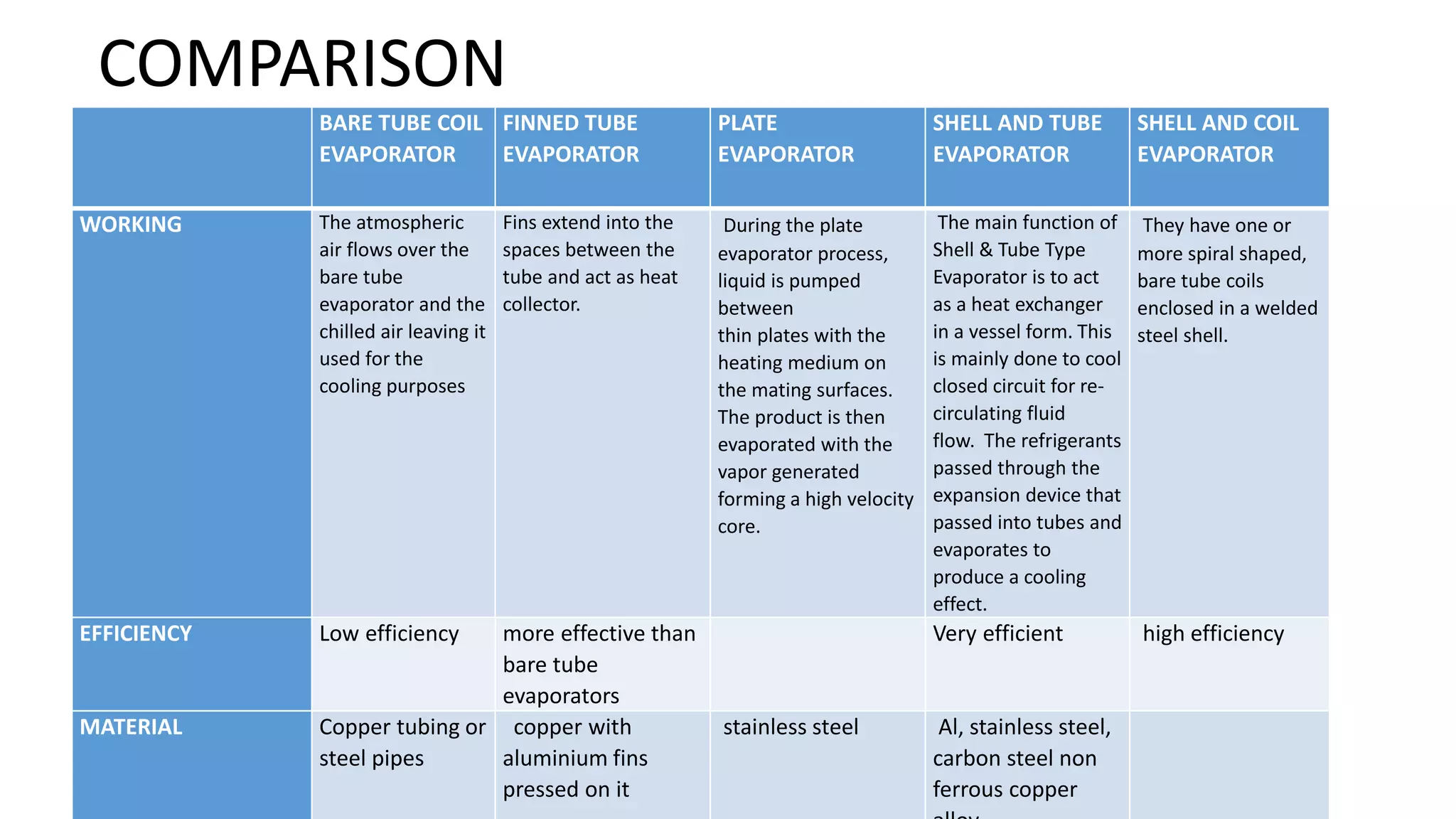
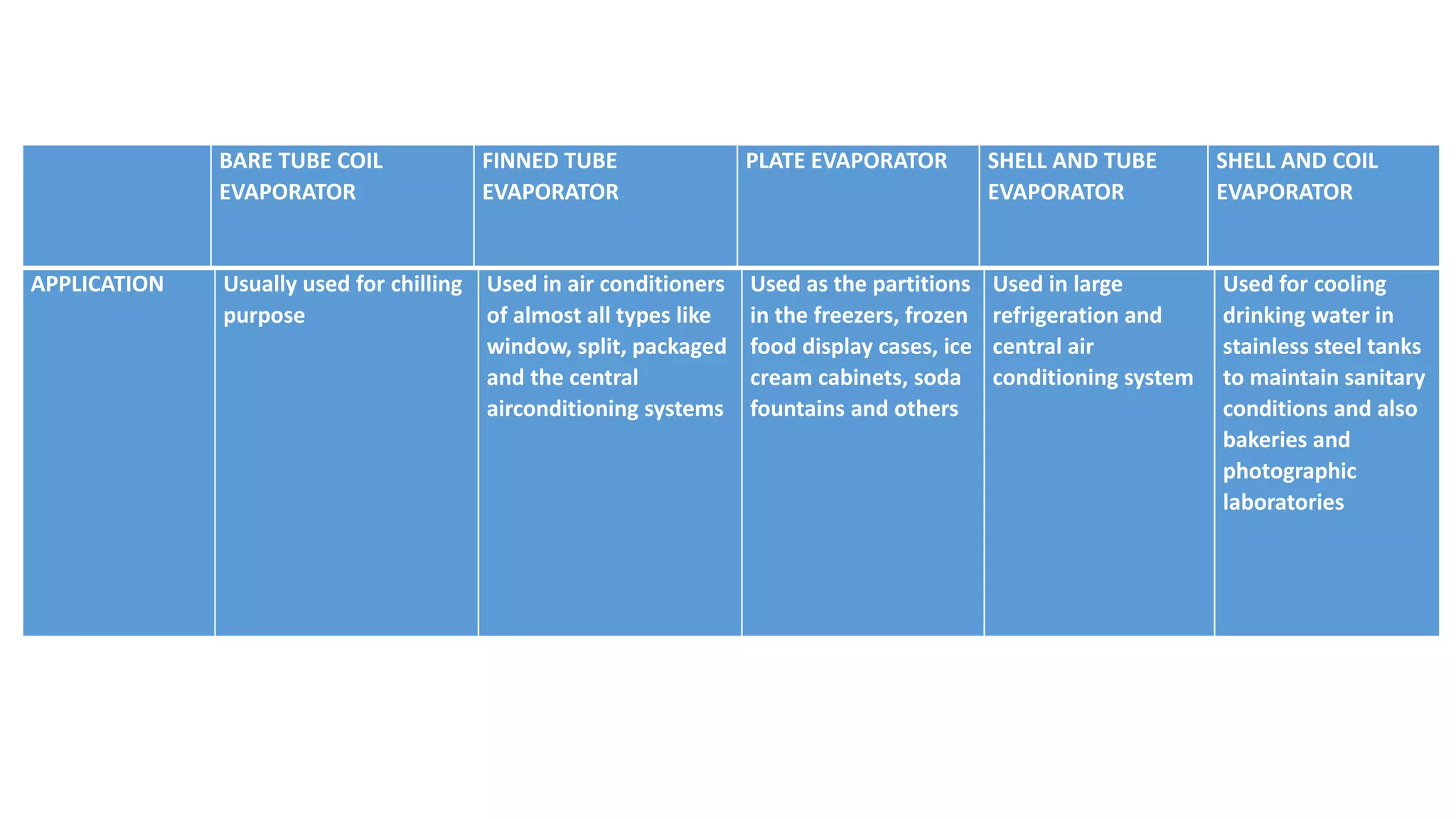
The evaporator is a key component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. It receives low-pressure refrigerant from the expansion valve and uses it to absorb heat from the surrounding air or liquid. There are several types of evaporators classified based on their design and heat transfer method, including bare tube, finned tube, plate, shell and tube, and shell and coil evaporators. Each type has advantages and disadvantages for different applications in areas like air conditioning, food freezing, and industrial cooling.