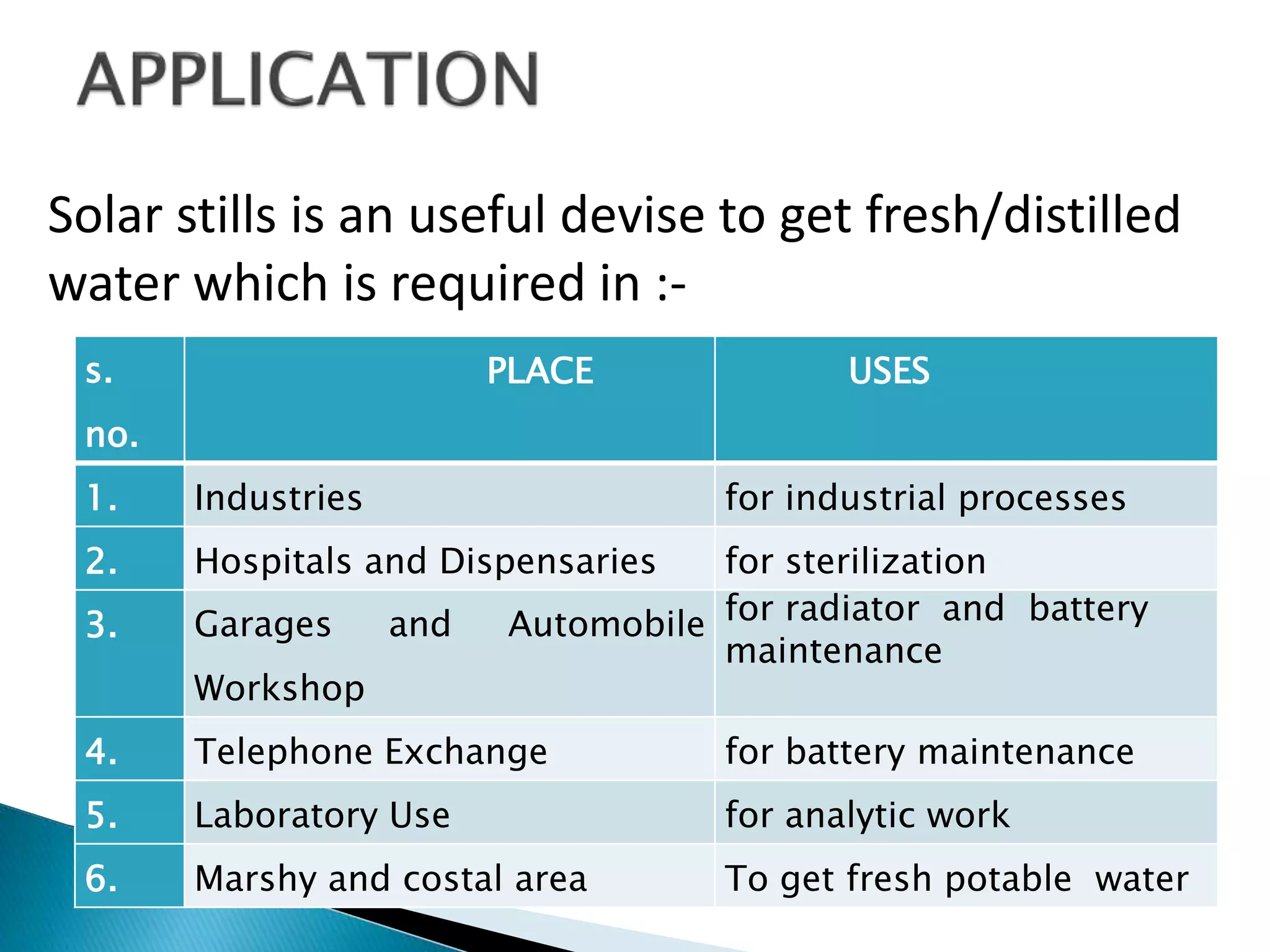
Solar distillation is the most reliable and least costly method of purifying contaminated water, especially in developing areas where fuel is scarce. The process uses solar energy to evaporate water which leaves impurities behind, then condenses the vapor into pure distillate. Various designs like single or multiple basin stills can be used, with efficiencies typically around 25-35%. While low cost, solar distillation has a disadvantage of low productivity that can be addressed through improvements to increase efficiency.