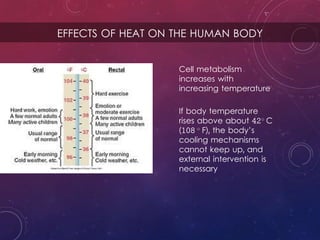
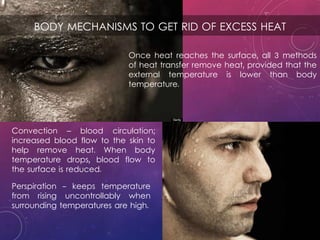
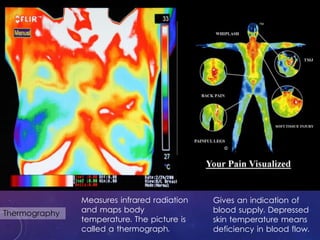
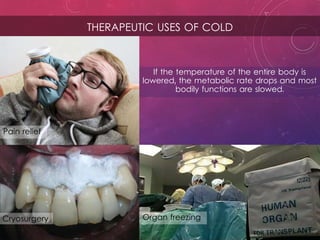
The document discusses the effects of heat on the human body, highlighting how cell metabolism increases with temperature and the body's cooling mechanisms become ineffective above 42°C. It explains methods of heat transfer such as convection and perspiration, and includes calculations on waste heat generated by students during a lecture. Additionally, it addresses the diagnostic and therapeutic uses of heat and cold, including their impact on infections and muscle relaxation.