Heat transfer in human body
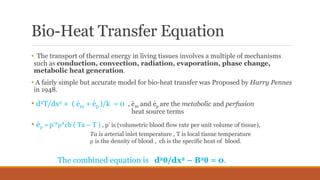
- 1. Bio-Heat Transfer Equation • The transport of thermal energy in living tissues involves a multiple of mechanisms such as conduction, convection, radiation, evaporation, phase change, metabolic heat generation. • A fairly simple but accurate model for bio-heat transfer was Proposed by Harry Pennes in 1948. • d2T/dx2 + ( ėm + ėp )/k = 0 , ėm and ėp are the metabolic and perfusion . heat source terms • ėp = p’*ρ*cb ( Ta – T ) , p’ is (volumetric blood flow rate per unit volume of tissue), Ta is arterial inlet temperature , T is local tissue temperature ρ is the density of blood , cb is the specific heat of blood. The combined equation is d2θ/dx2 – B2θ = 0.
- 2. Lungs • Analogous to Heat Exchanger. • Heat transfer between warm blood and cool air. • Combined surface area of its various alveoli and ducts is approximately equal to 80 square meters
- 3. Body loses both sensible heat by convection and latent heat by evaporation from the lungs, and these can be expressed as The rate of total heat loss from the lungs through respiration can also be expressed approximately as
- 4. Effects of the ventilation pattern and pulmonary blood flow on lung heat transfer -V. B. Serikov and W. Fleming Ventilation: Ventilation is a process of "processing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality . Pulmonary blood flow: Pulmonary arteries carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. So blood flow through pulmonary artery is pulmonary blood flow. Perfusion: Perfusion is the process of a body delivering blood to a capillary bed in its biological tissue. Its basically the passage of a fluid through the vessels of a specific organ.
- 5. Experimental Setup to calculate HTC
- 6. VT=Tidal Volume(Volume of air moved in or out of the lung during breathing)
- 7. Where J=The total heat flux from the lung Tb=Blood temperature Tge=Temperature of exhaled air Tgo=Temperature of inhaled air n=n molar ratio of water vapor in the gas H=heat of water vaporization Heat transfer in the bronchial wall is given by Overall Lung Heat Transfer Coefficent w=effective thermal conductivity r=radial coordinate
- 8. Temperature variation along respiratory track
- 9. The Human Cardiovascular System as Counter Current Heat Exchanger • In order to prevent the core body temperature from reducing significantly, the cardiovascular system is organized as a counter-current heat exchanger. • This organization has been observed in many species (including all warm-blooded animals) • In this design, one artery is always paired and adjacent to one vein. • This mechanism plays a primary role when the external environmental temperature diverge significantly from the core body temperature in all warm- blooded animals.
- 10. Mechanism of Cardiovascular System as Heat Exchanger • In colder environment the human’s extremities (hands, fingers, toes, etc.) will be at a higher temperature than the environment. • The temperature of the tissue in the extremity and importantly the blood in the veins will be lower than the temperature of blood in the arteries • Due to eat transfer between the artery and vein, the arterial blood temperature begins to reduce, at the same time, the venous blood would begin to be rewarmed. •This results in the venous blood returning to the core at a higher temperature than it would have without the heat transfer between the artery and vein in a counter-current mechanism. •Thus the net heat transfer to the environment is reduced through the actions of the cardiovascular counter-current heat exchanger.
- 11. Equations for the Cardiovascular System • Q = U As ΔTm • Q blood = mcp dT/dx • Combining the two equation we get, Q + Q blood= U As ΔTm + mcp dT/dx • So individual equations are, equations, mcp dTA/dx + (UAs)AV(TA-Tv) + (UAs)AV(TA-To) = 0 (for artery) mcp dTv/dx - (UAs)AV(TA-Tv) + (UAs)AV(TV-To) = 0 (for vein) These are system of linear ordinary differential equations, which can be solved using standard methods to obtain the artery and vein temperatures.
- 12. Heat Losses From Human Body • The metabolic heat generated in the body is dissipated to the environment through the skin and the lungs by convection and radiation as sensible heat and by evaporation as latent heat. •Sensible heat loss from the skin depends on the temperatures of the skin, the environment, and the surrounding surfaces as well as the air motion. The latent heat loss, on the other hand, depends on the skin wettedness and the relative humidity of the environment as well.
- 14. Human Thermal Comfort •Average core temperature of 37 ±0.5 degrees Celsius, or 98.2 ±1.3°F. •Less than normal produces severe shivering, poor coordination, and again confusion and even death. • More than normal into heat stroke, producing dehydration, confusion, and eventually even death.
- 15. Depends on Clothing Climate Physical Activity The human body converts the chemical energy of its food into work and heat. The amount of heat generated and lost varies markedly with activity and clothing levels.
- 16. Role of Insulation •If the air around our bodies were completely still (and if we too kept completely still), then that air would act as a pretty good heat insulator, and we would stay nice and warm. •But air being a fluid naturally moves around, and the movement of air carries heat away from our bodies by a process called convection. •On a windy day, the atmosphere of warmer air near our bodies is carried away, and it is replaced by cooler air, thus speeding the loss of heat. That’s why the wind chill factor is a relevant measure of how cool the air feels on a cold, windy day.
- 17. Providing Insulation •When we wrap our bodies in layers of wool or down, we surround ourselves with a huge number of tiny air pockets. The fibers or feathers between those air pockets block the movement of air from pocket to pocket, thus reducing the flow of heat by convection within the material. •Convection can still carry heat away from the surface of a sweater or jacket, but the temperature is lower there than at the surface of our bodies, so there is less heat loss by convection than if we were naked or wearing less insulating clothing.
- 18. Different types of clothing • One famed property of wool is that it still insulates when wet, unlike cotton which only insulates well when dry. Why is this? •Synthetic fiber insulation ◦ Thinsulpahte ◦ Primaloft
- 19. Convection with clothing • Convection heat transfer Q’= Acl. hc . (Tcl - Ta) where, hc= heat transfer coefficient , Tcl =clothing temperature, Ta =ambient air temperature, Acl =clothing area factor. Radiation with clothing Qr’ = σ . εcl . Acl . Fvf [(Tcl + 273.15)^4 + – (Tr + 273.15)^4] where σ= Stephen-Boltzmann constant, εcl= Emissivity of clothing, Fvf= View factor,
- 20. Clothing Surface Temperature Conduction from inner surface to outer surface of clothing Qc’ = (Tsk – Tcl) / Rcl loss to environment Qc’=Q’+Qr’
- 21. Activity W/m2 W1) Btu/hr1) Met Reclining Sleepimng 46 83 282 0.8 Seated relaxed 58 104 356 1.0 Standing at rest 70 126 430 1.2 Sedentary activity (office, dwelling, school, laboratory) 70 126 430 1.2 Car driving 80 144 491 1.4 Graphic profession - Book Binder 85 153 522 1.5 Standing, light activity (shopping, laboratory, light industry) 93 167 571 1.6 Teacher 95 171 583 1.6 Domestic work -shaving, washing and dressing 100 180 614 1.7 Walking on the level, 2 km/h 110 198 675 1.9 Standing, medium activity (shop assistant, domestic work) 116 209 712 2.0 Building industry - Brick laying (Block of 15.3 kg) 125 225 768 2.2 Washing dishes standing 145 261 890 2.5 Domestic work - raking leaves on the lawn 170 306 1043 2.9 Domestic work - washing by hand and ironing (120-220 W) 170 306 1043 2.9 Iron and steel - ramming the mould with a pneumatic hammer 175 315 1075 3.0 Building industry -forming the mould 180 324 1105 3.1 Walking on the level, 5 km/h 200 360 1228 3.4 Forestry -cutting across the grain with a one-man power saw 205 369 1259 3.5 Volleyball Bicycling (15 km/h) 232 418 1424 4.0
- 22. Bibliography • MODELLING HEAT TRANSFER IN HUMANS - A.J.H. Frijns, G.M.J. van Leeuwen and A.A. van Steenhoven •Effects of the ventilation pattern and pulmonary blood flow on lung heat transfer AUTHOR(S) - Serikov, V. B.; Fleming, N. W •https://en.wikipedia.org/ •http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/heatreg.html •http://www.bbc.co.uk/education/guides/zttrd2p/revision/5 •Heat and Mass Transfer Fundamentals and Applications 5th edition – Yunus Cengel
- 23. Thank You
Editor's Notes
- Human thermal comfort depends on combinations of clothing, climate, and physical activity [13]. The human body converts the chemical energy of its food into work and heat. The amount of heat generated and lost varies markedly with activity and clothing levels
