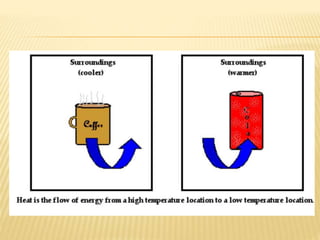
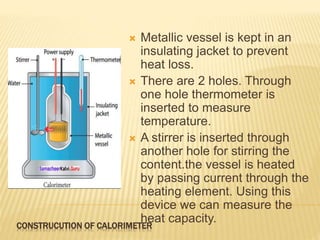
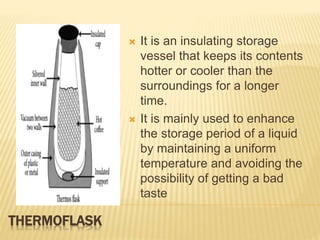
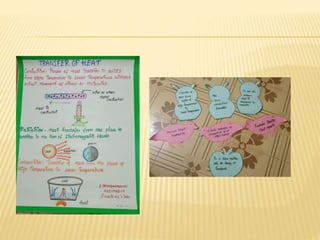
This document discusses different methods of heat transfer - conduction, convection, and radiation. It provides examples of each in daily life and defines key related terms like temperature, units of heat, calorimetry, calorimeter, thermostat, and thermoflask. Conduction occurs through direct contact between objects and involves the transfer of kinetic energy between adjacent particles. Convection involves the movement of molecules or atoms within fluids like liquids and gases. Radiation can transfer heat through empty space via electromagnetic waves.