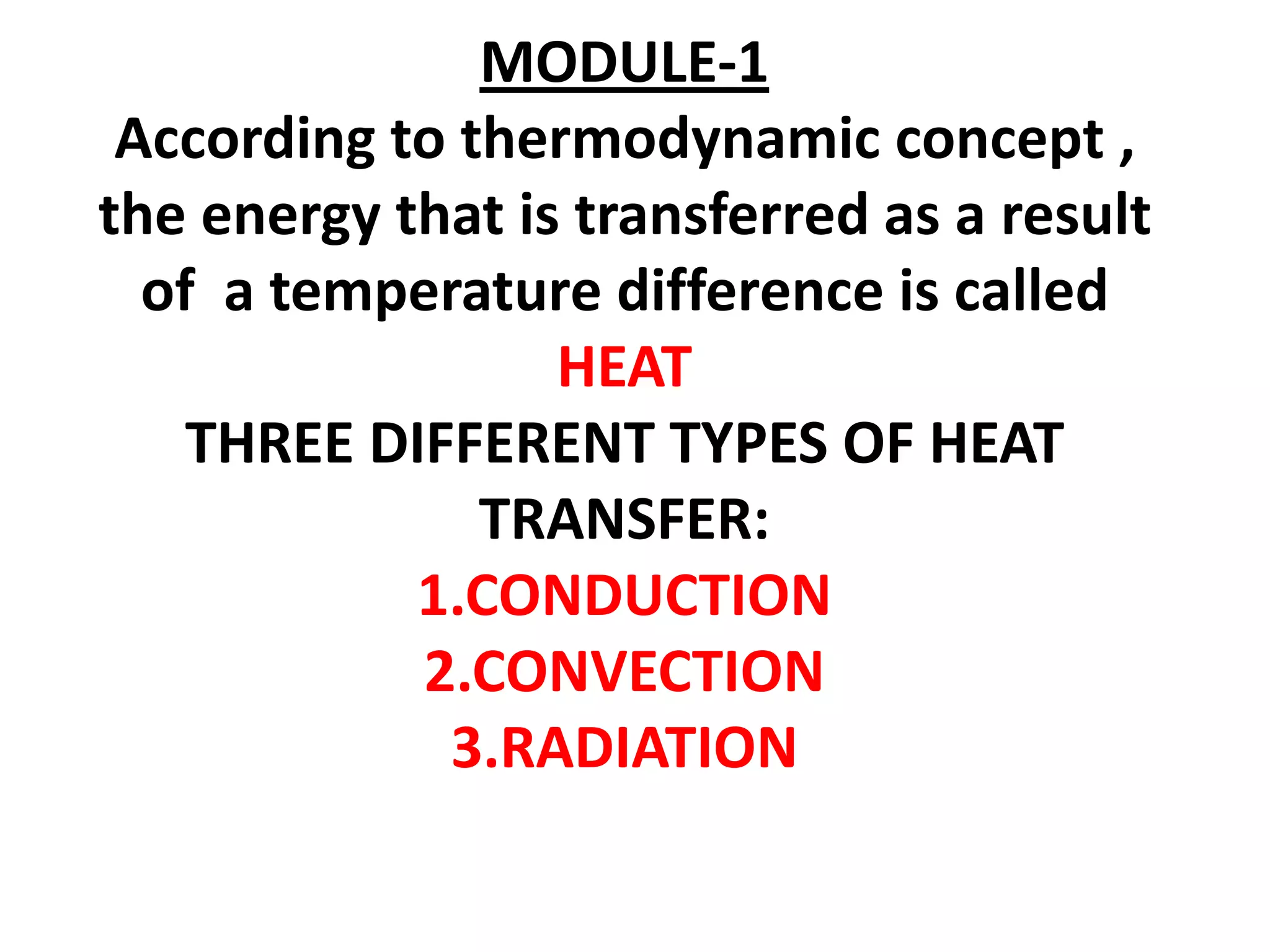
1. Heat transfer occurs through three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation.
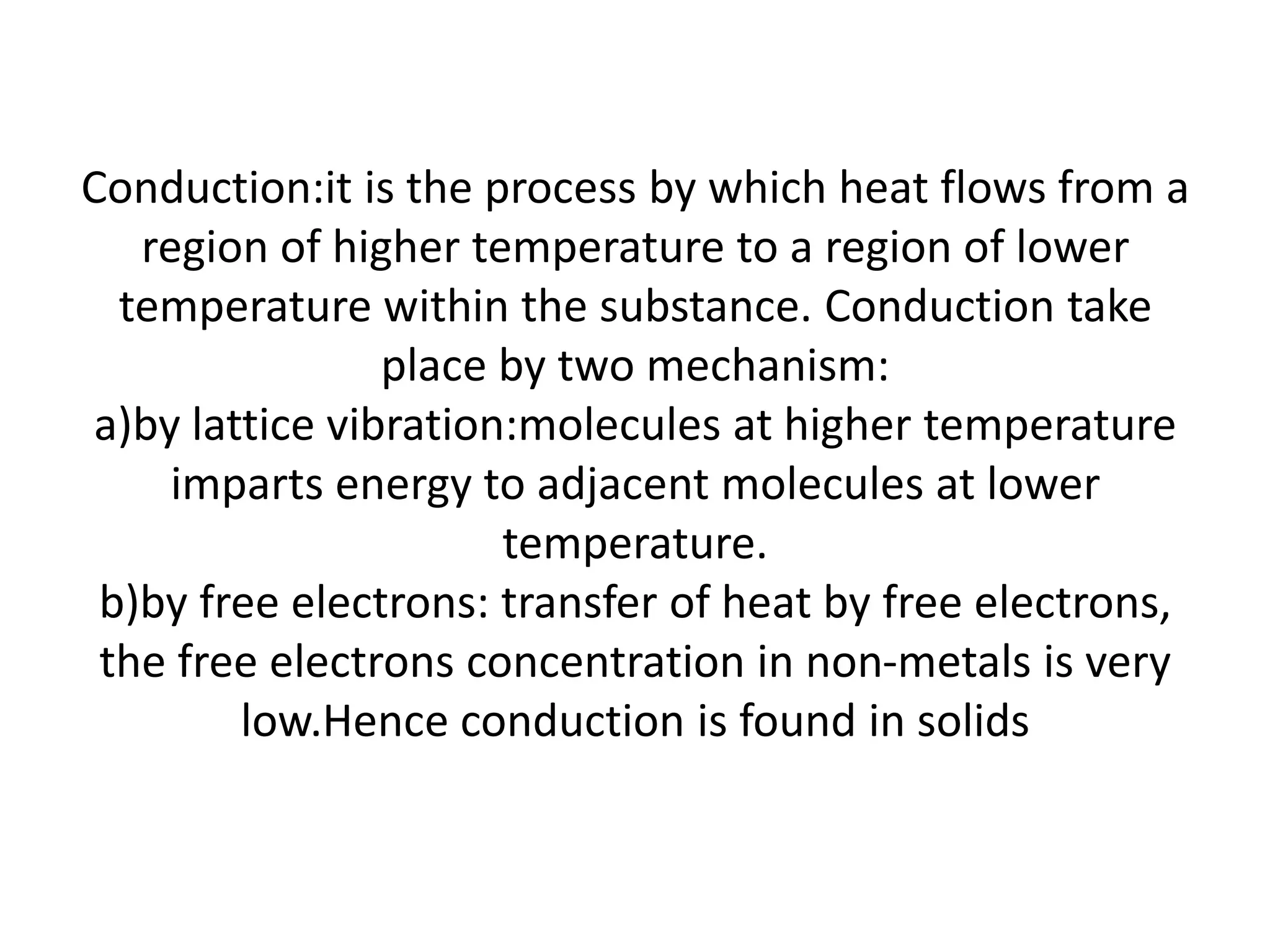
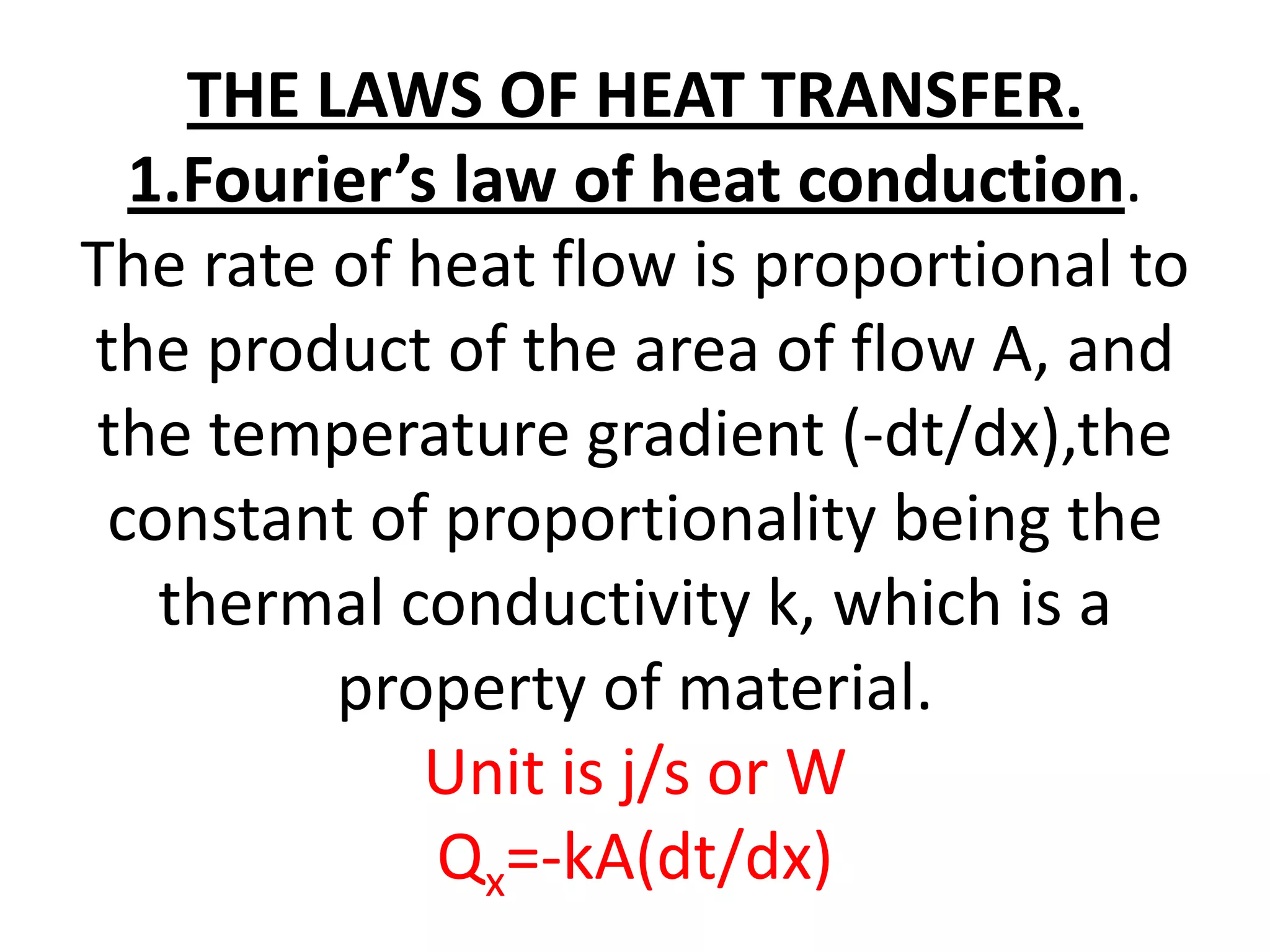
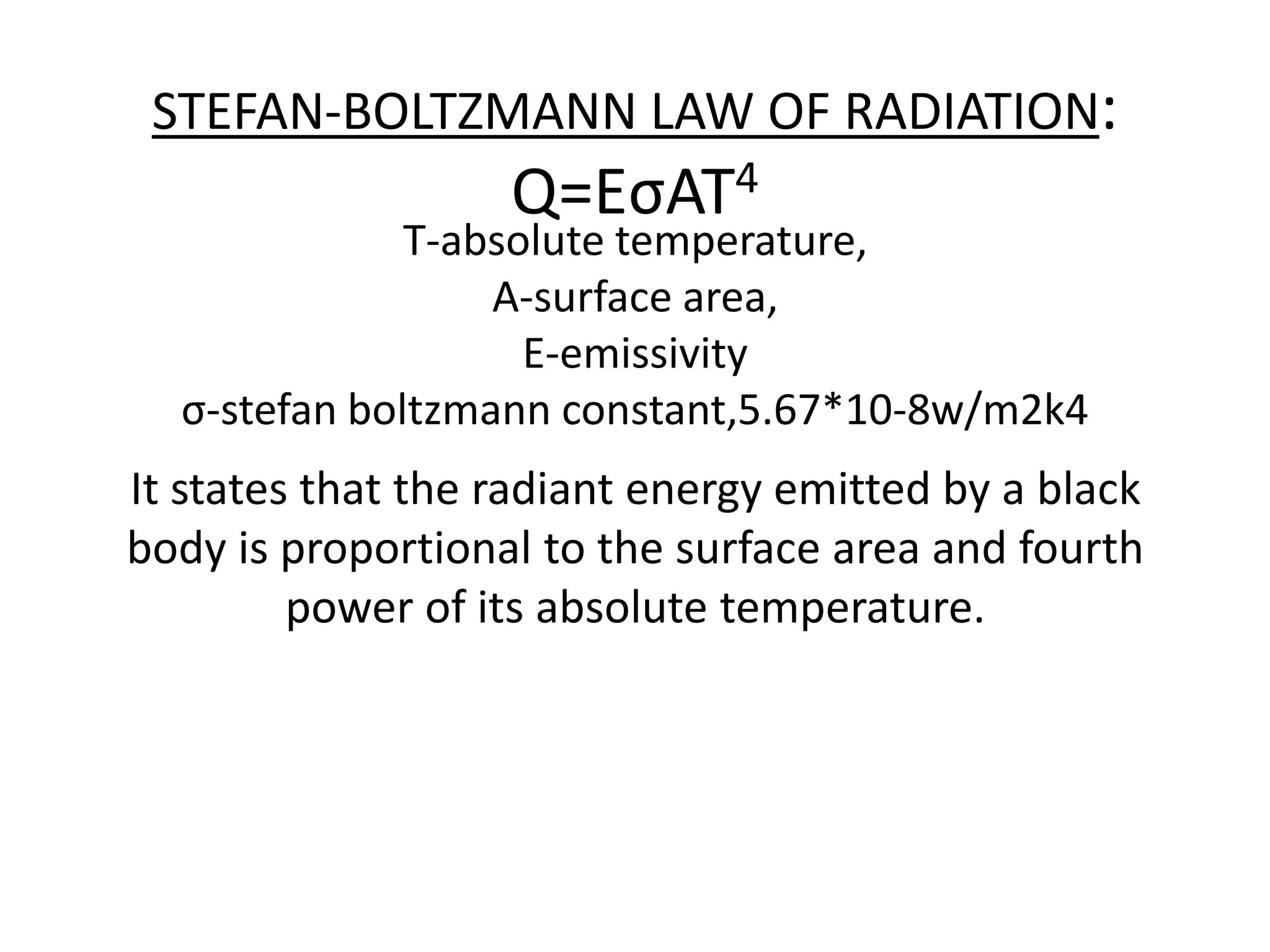
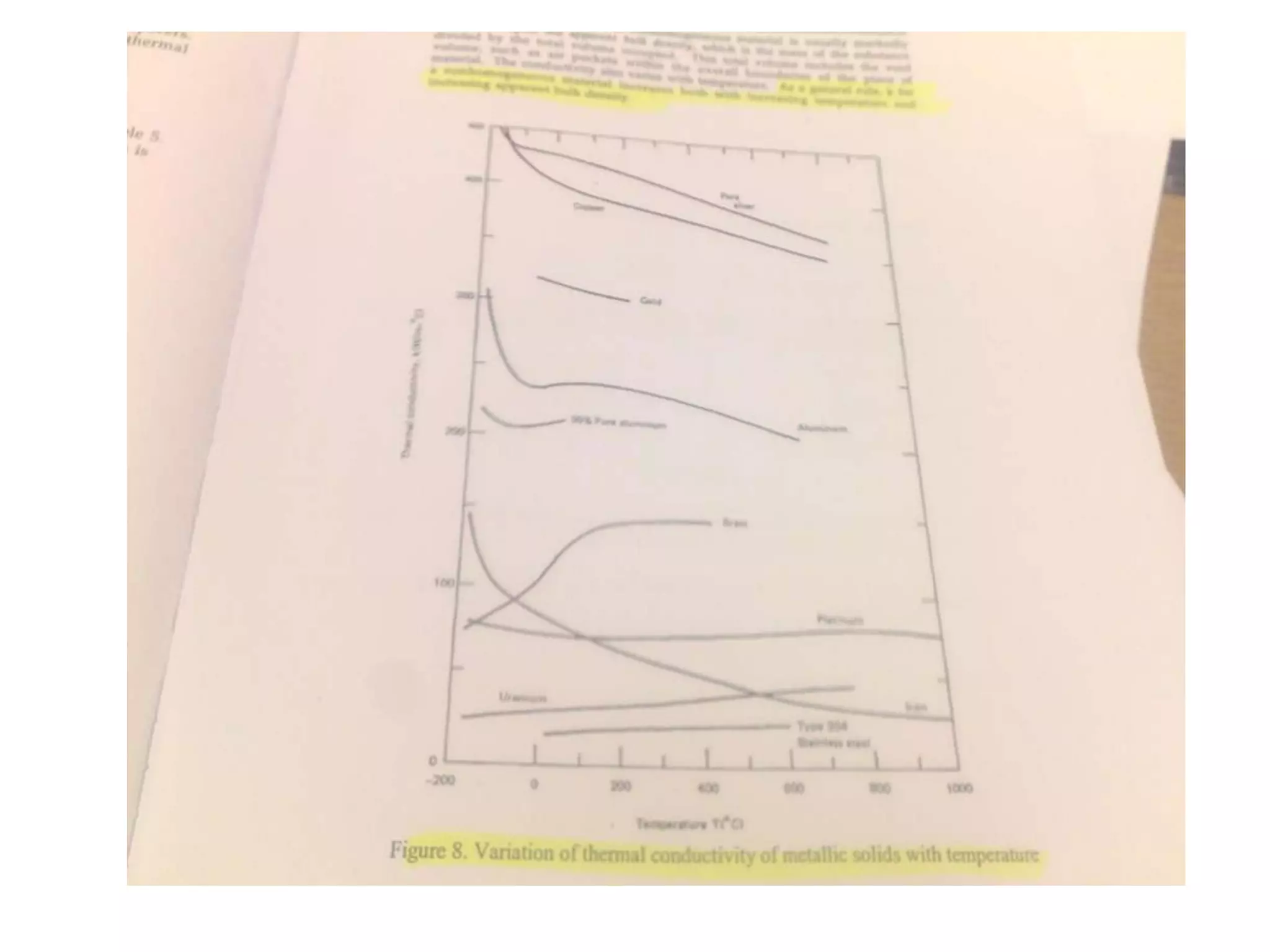
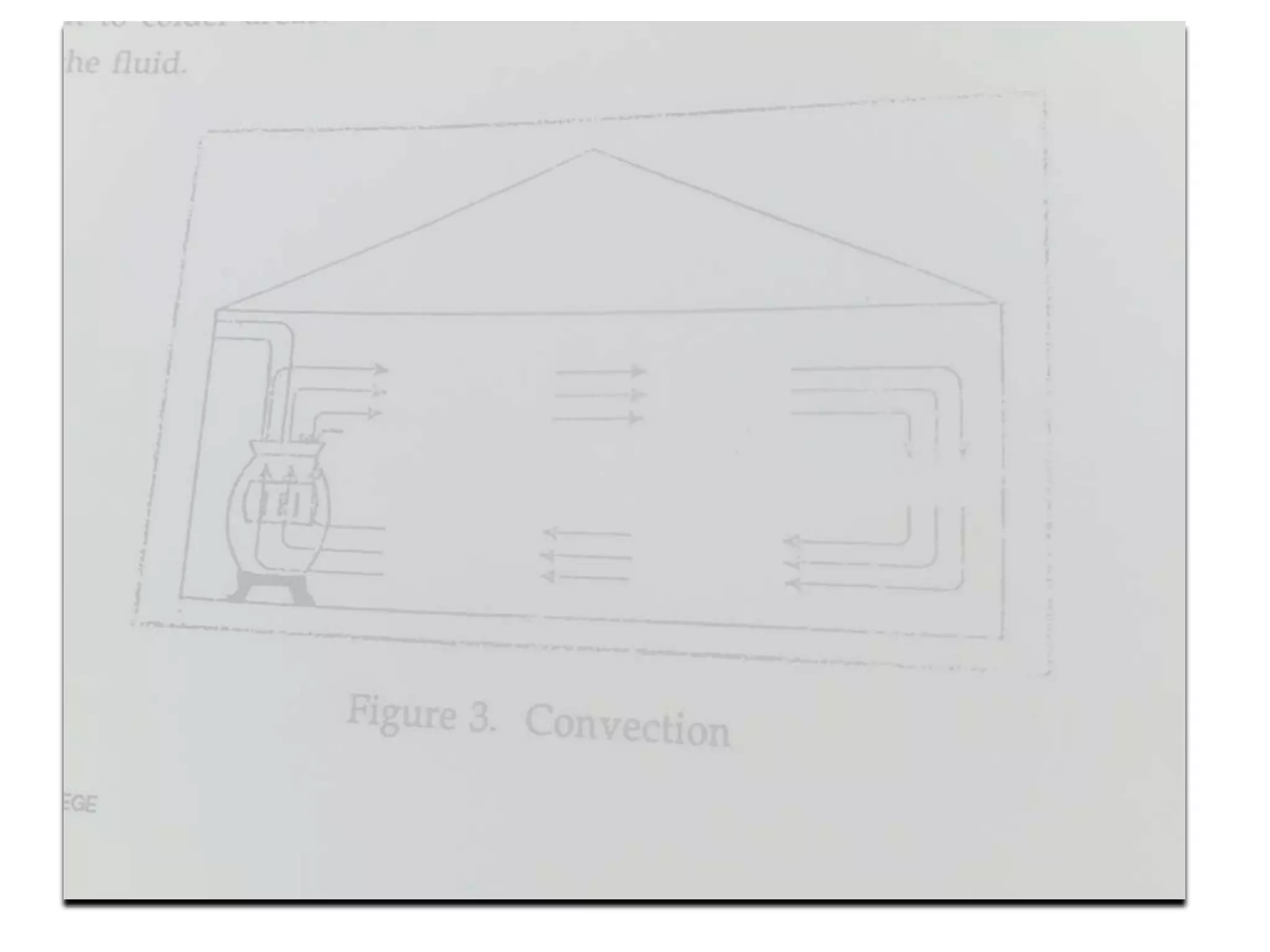
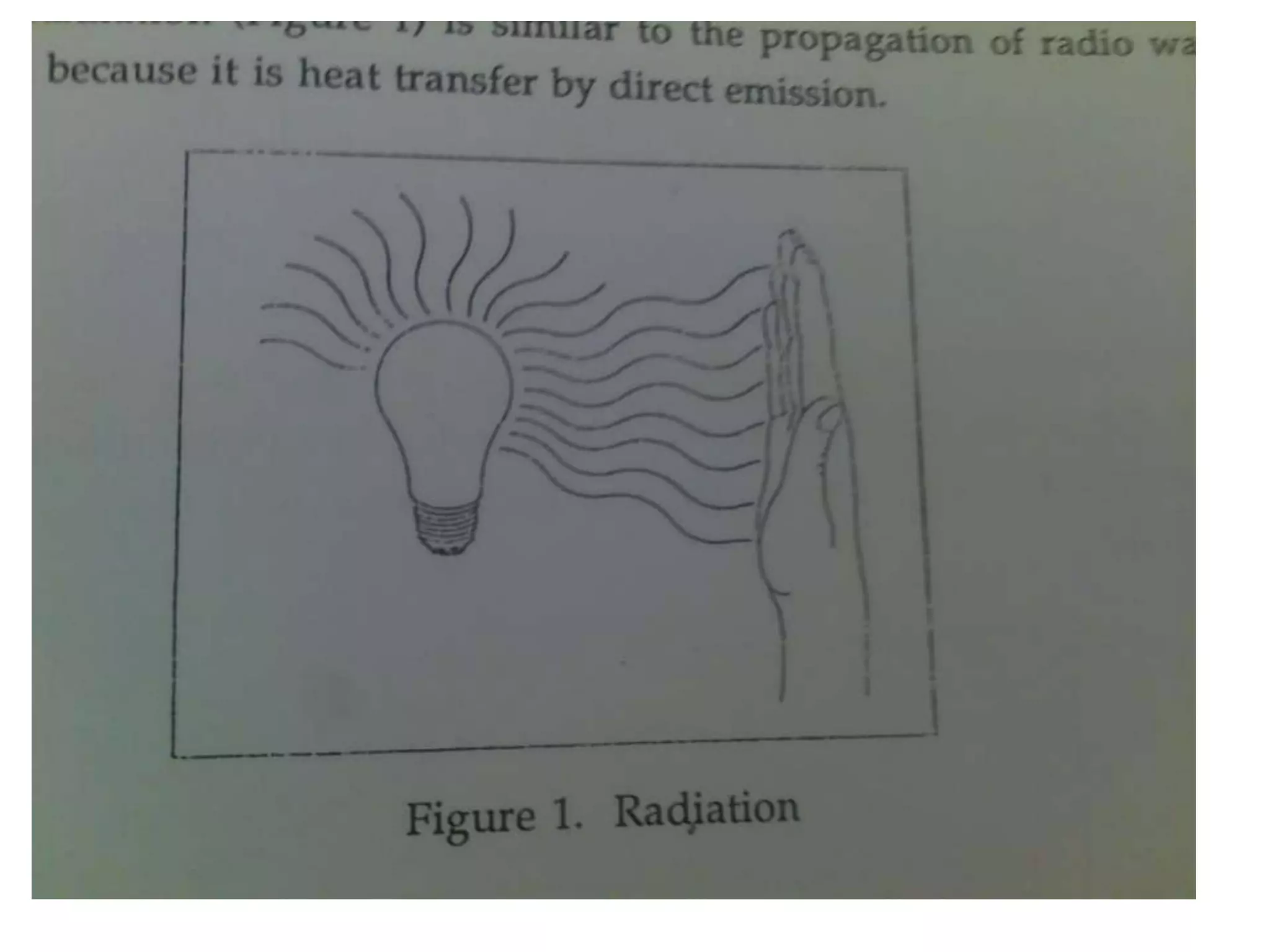
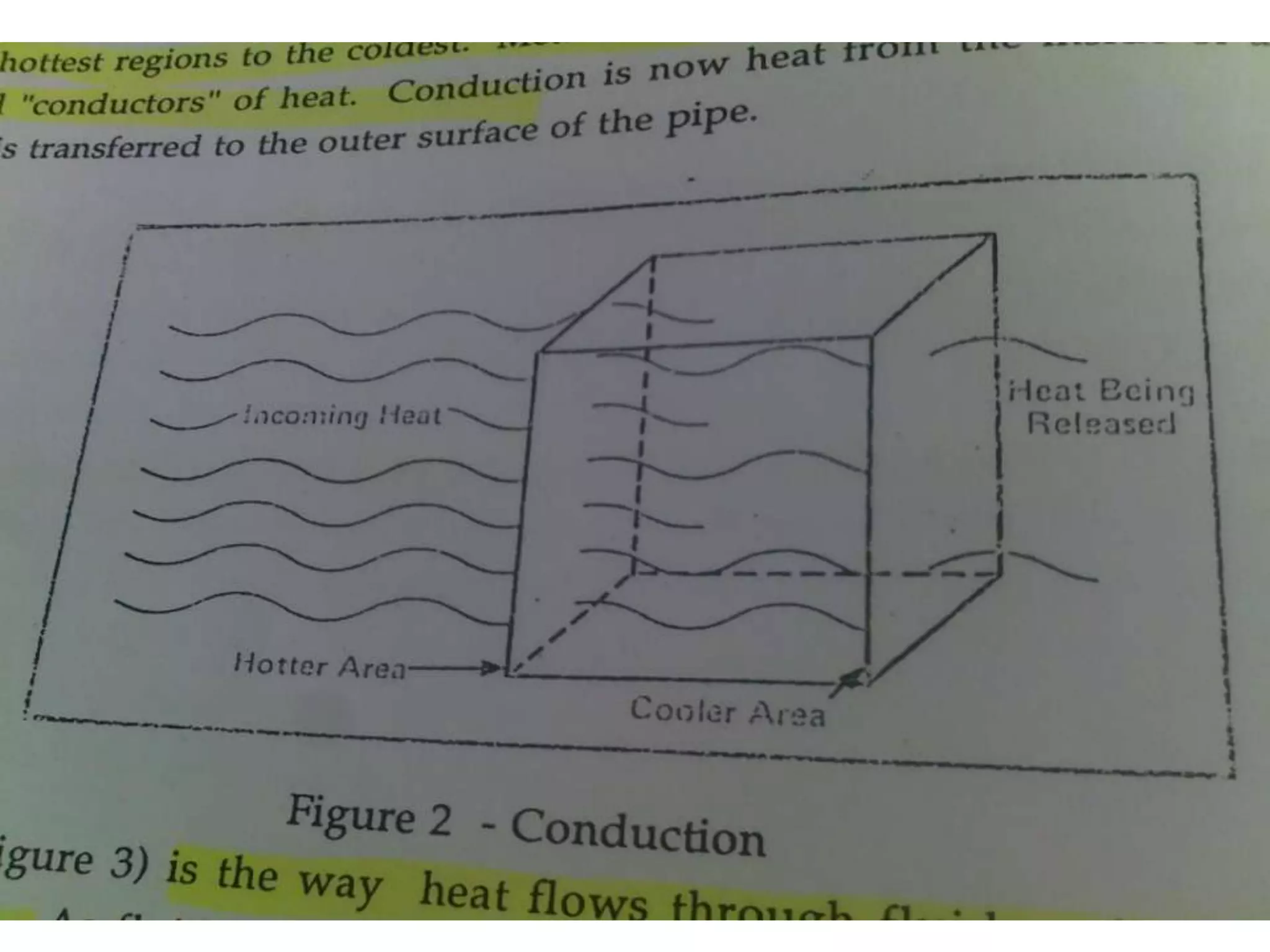
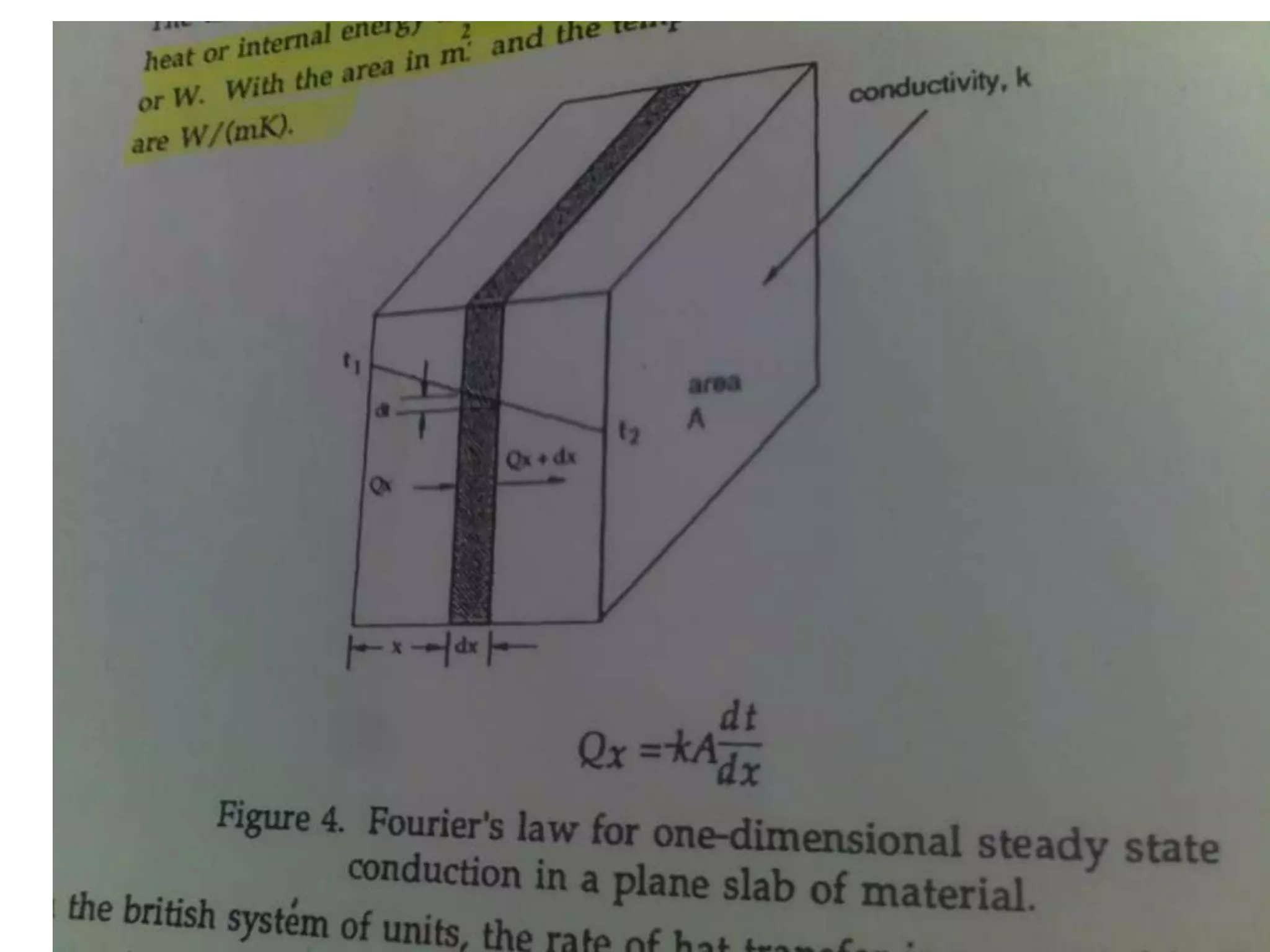
2. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact of particles. Convection involves the transfer of heat by fluid motion. Radiation involves heat transfer through electromagnetic waves without a medium.
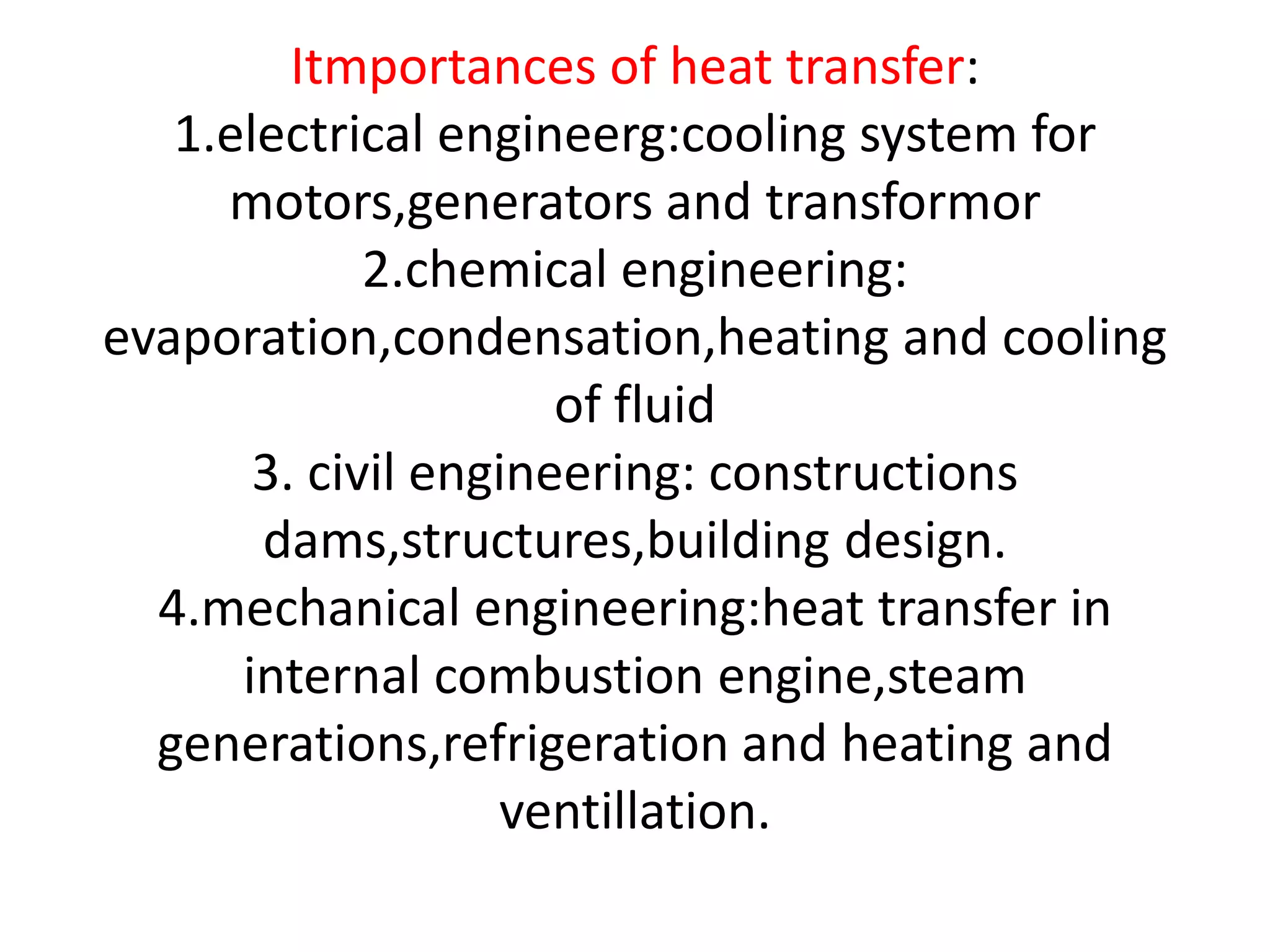
3. Heat transfer is important across several engineering disciplines for applications like cooling systems, fluid heating/cooling, building design, and engines.