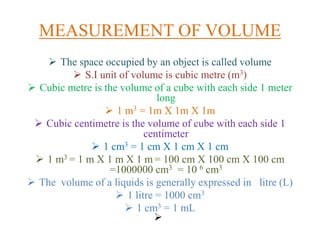
The document provides an overview of measurement concepts in physics, focusing on volume, area, density, and speed. It includes definitions, units of measurement, key formulas, and example problems to illustrate calculations related to these concepts. Homework questions are also provided for students to reinforce their understanding.
























![2.A solid silver piece is immersed in water
contained in a measuring cylinder. The level of
water rises from 50 ml to 62 ml. Find the volume
of silver piece.
Ans. Volume of the silver piece = (62 − 50) [1 ml
= 1 cm3 ] = 12 ml = 12 cm3
3.Find the volume of a liquid present in a dish of
dimensions 10 cm X 10 cm X 5 cm.
Ans. Volume of liquid = Volume of dish =
(10 X 10 X 5) = 500 cm3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class7physicalquantitymeasurement-201121063521/85/Class-7-PHYSICAL-QUANTITY-MEASUREMENT-26-320.jpg)

![ 7.The mass of an iron ball is 312g. The density of iron
is 7.8 g/cm3 . Find the volume of the ball.
Ans. Volume of the ball = 312/7.8 = 40 cm3
8. A cork has volume 25 cm3. The density of the cork
0.25 g/cm3. Find the mass of the cork.
Ans. Mass of the cork = (25 X 0.25) = 6.25 g.
9. Mass of 5 litre of water is 5 kg. Find the density of in
g/cm3.
Volume = 5 L = 5000 ml = 5000 cm3
[1 ml = 1 cm3 ]
Mass = 5 kg = 5000 g
Density = 5000/5000 = 1 g/cm3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class7physicalquantitymeasurement-201121063521/85/Class-7-PHYSICAL-QUANTITY-MEASUREMENT-28-320.jpg)







