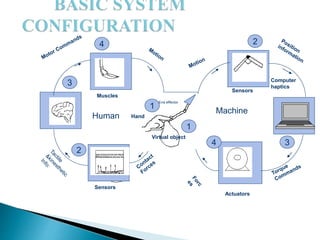
This document discusses haptics technology, which adds the sense of touch to virtual environments. It provides an introduction to haptics and its history, describes how haptic devices create virtual environments and simulate the sense of touch, lists some common haptic devices and their applications, discusses limitations, and concludes by anticipating future advances in haptics.