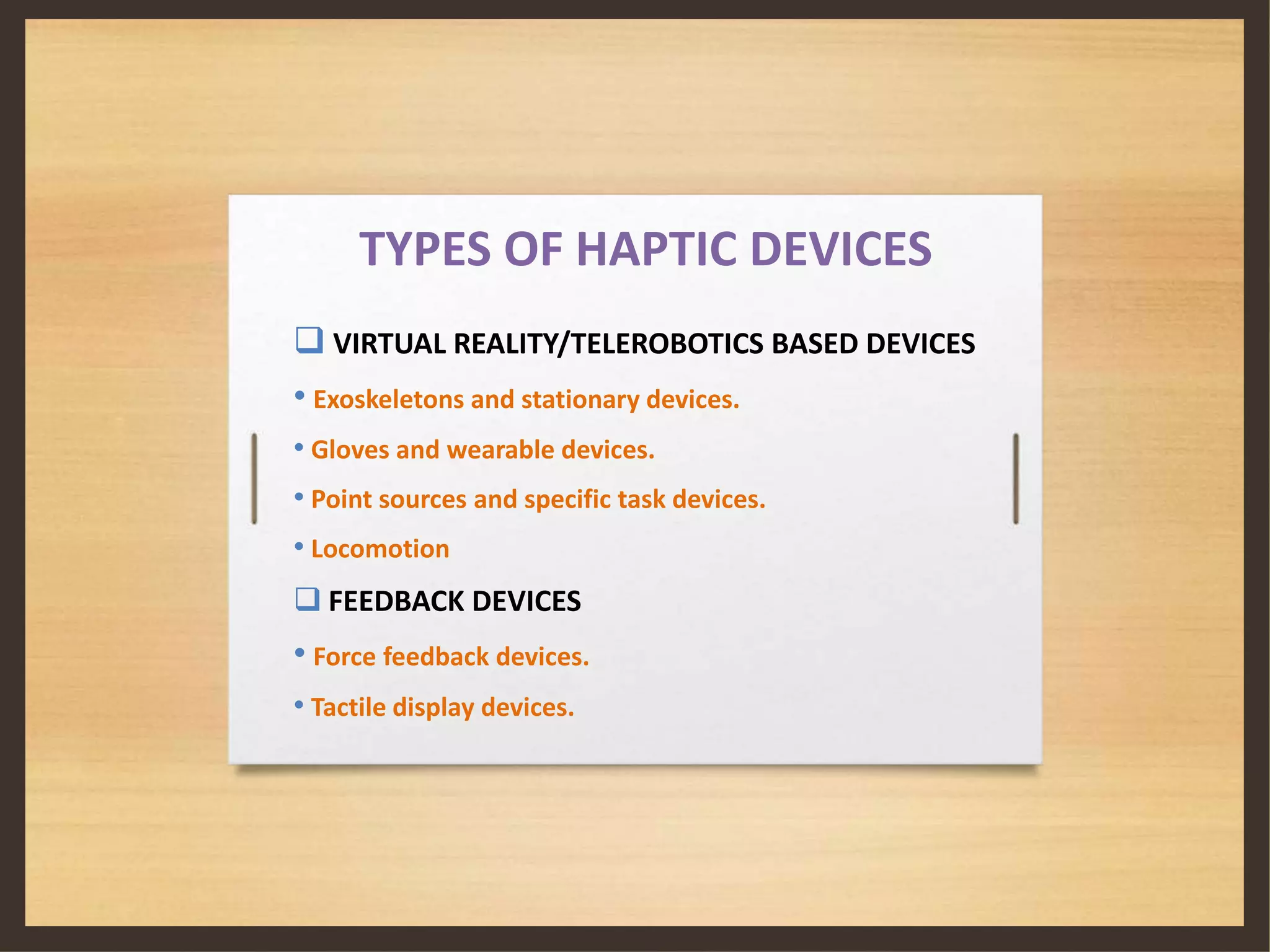
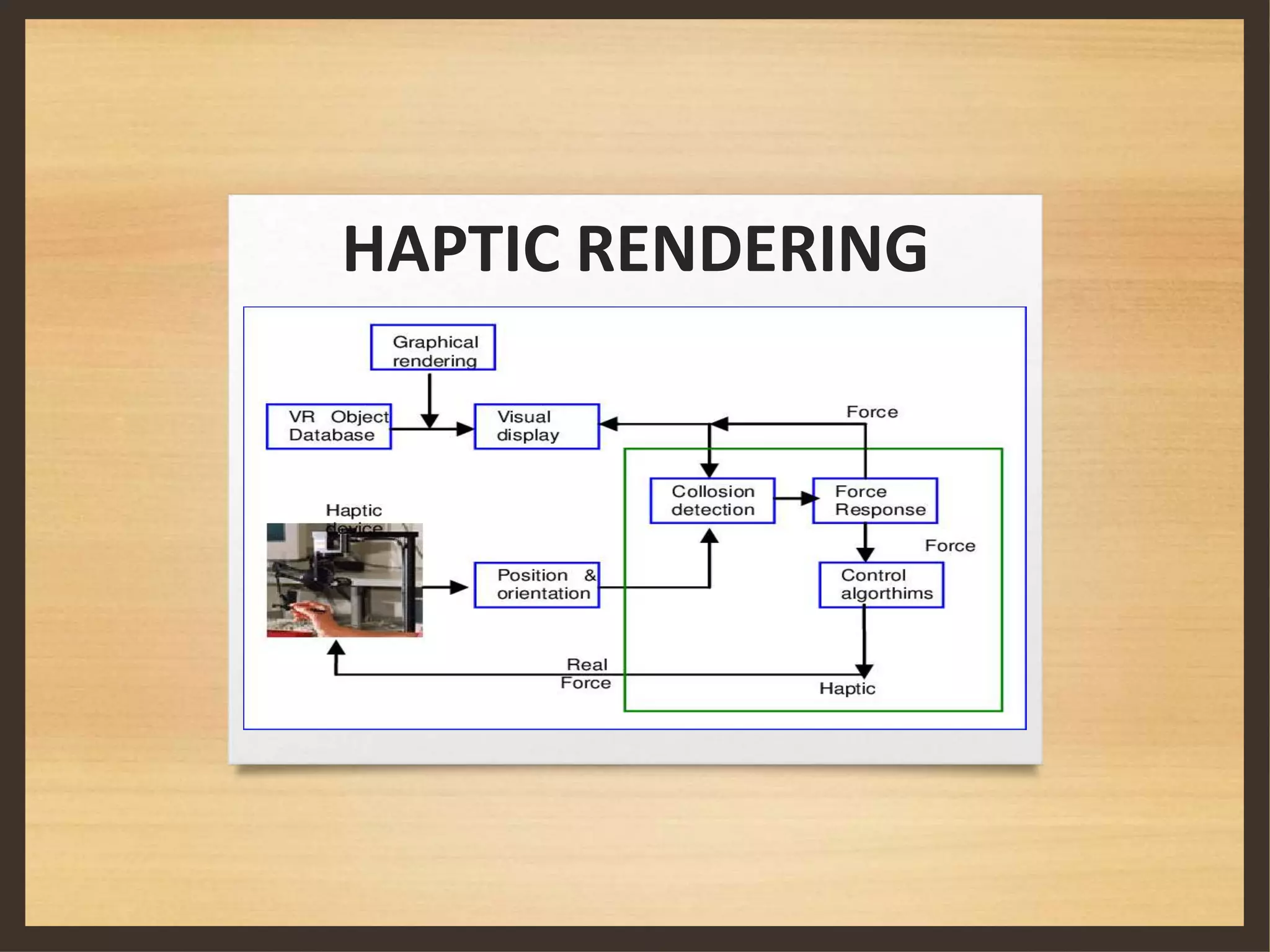
This document discusses haptic technology, which adds the sense of touch to virtual objects. It begins by defining haptics and explaining how it allows virtual objects to seem real when touched. The document then covers the history of haptics, including early uses in aircraft controls and the Apple Watch. It describes how haptics combines tactile and kinesthetic information. Different types of haptic devices are presented, including gloves and tools that allow users to touch and feel virtual 2D and 3D objects. Limitations and applications of haptic technology are also summarized.