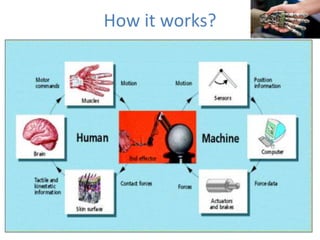
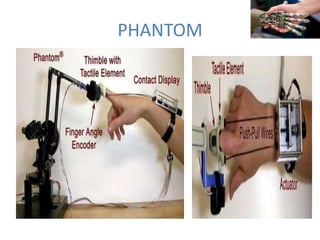
Haptic technology interfaces users with virtual environments through the sense of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions. It works by using haptic devices like Phantom, a robotic arm that provides mechanical stimulation, or CyberGlove, which tracks hand gestures. Applications of haptics include surgical simulation, medical training, and graphical user interfaces. The technology provides advantages like easy access and use as well as conservation during development, but also has disadvantages such as limited magnitude, expense, and complexity.