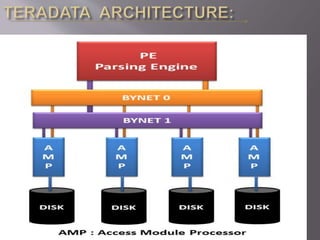
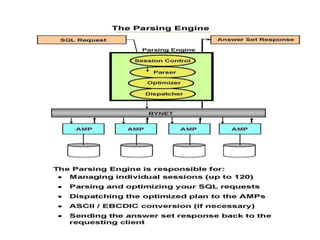
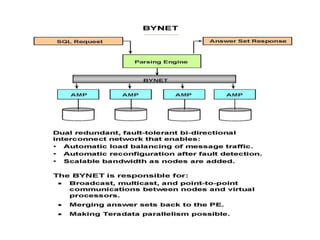
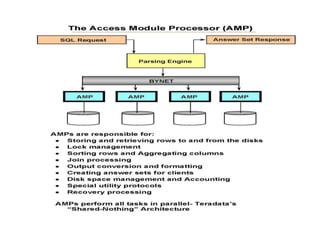
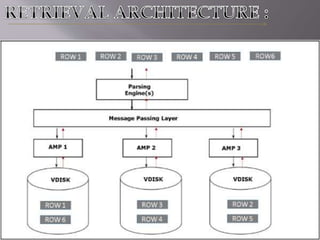
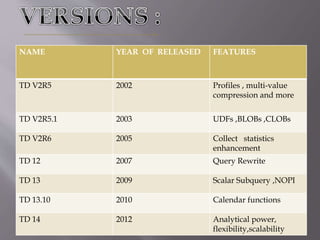
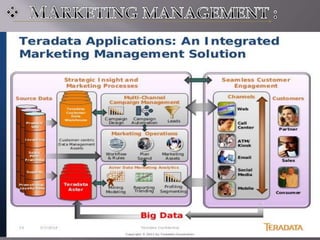
This document discusses Teradata, an RDMS designed for large commercial databases. It provides a brief history of Teradata starting in 1979 and its acquisition by NCR in 1992. It also lists versions released from 2002-2012 and their new features. The advantages are its parallel processing capacity to handle large loads and queries concurrently. It has a shared nothing architecture providing high fault tolerance. Disadvantages include its lack of suitability for small transactions and higher costs. The conclusion states Teradata makes creating and dropping tables easy for data warehousing.