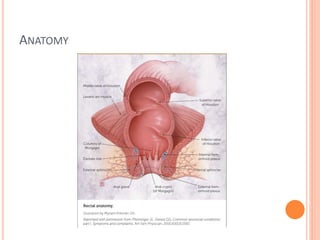
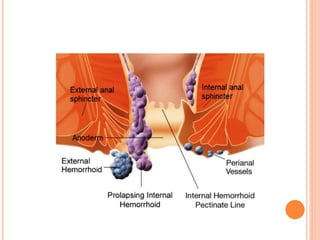
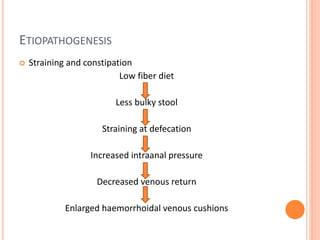
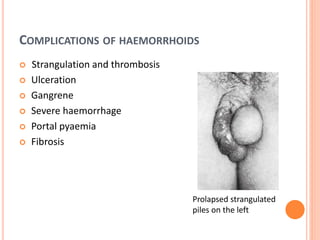
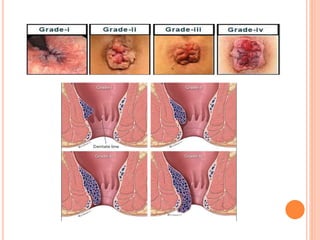
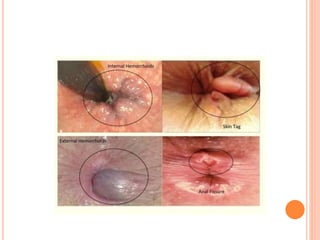
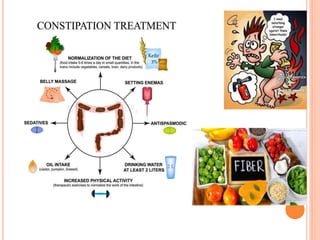
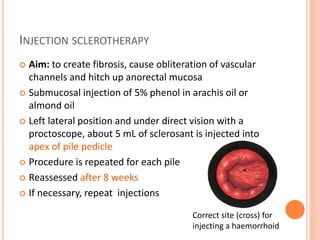
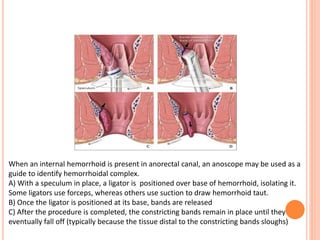
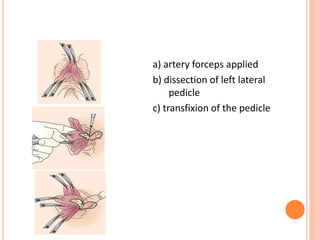
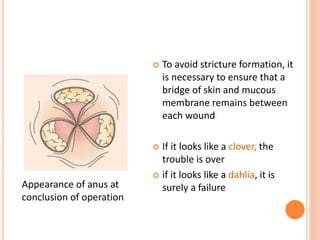
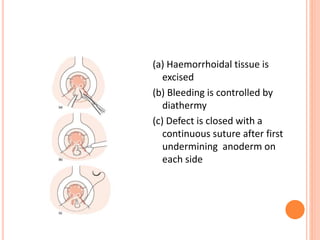
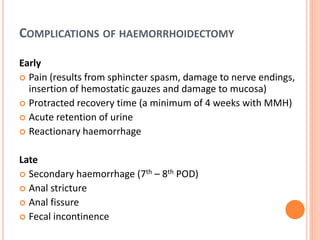
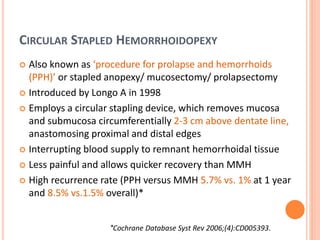
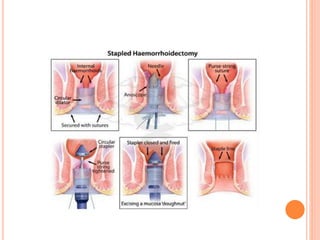
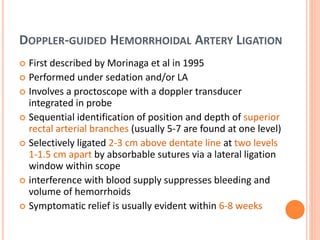
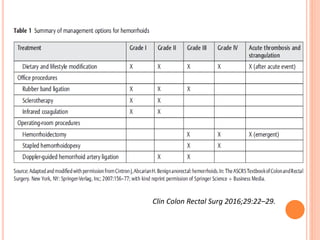
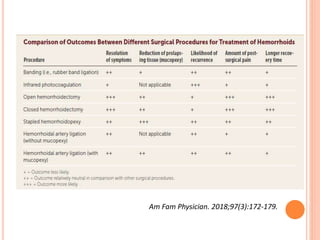
This document discusses haemorrhoids, including their anatomy, classification, etiology, clinical features, complications, grading, and treatment options. Haemorrhoids are classified as internal or external depending on their location relative to the dentate line. Common causes include straining during bowel movements and sedentary lifestyles. Clinical features may include bleeding, pain, irritation, and prolapse. Treatment ranges from conservative options like lifestyle changes to surgical procedures like rubber band ligation, injection sclerotherapy, and haemorrhoidectomy. Complications of haemorrhoidectomy can include pain, stricture, and incontinence.