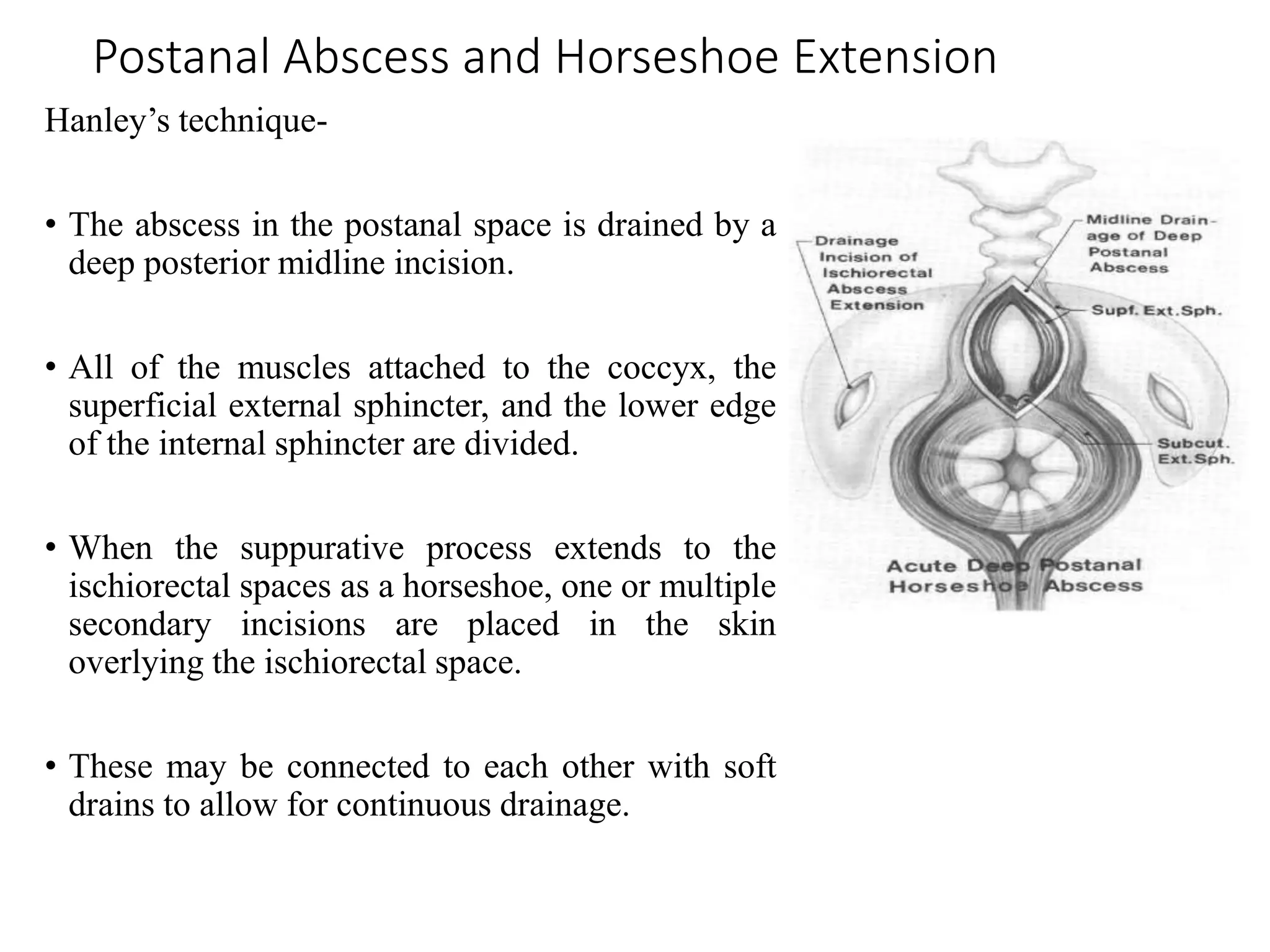
This document provides information about perianal abscesses including their etiology, pathogenesis, classification, clinical presentation, investigations, and management. Anorectal abscesses are infections of the soft tissues around the anus that form abscess cavities. They commonly originate from infections of anal glands. Abscesses are usually drained surgically with antibiotics added for immunosuppressed individuals. The type of drainage depends on the abscess classification. While some advocate primary fistulotomy, others prefer delayed fistulotomy after initial incision and drainage to avoid unnecessary procedures.