This document provides information about haemorrhoids (also known as piles), including:
1. Haemorrhoids are varicosities of the veins in the anal canal that are common, affecting around 25% of adults. Risk factors include constipation, pregnancy, liver disease, and heredity.
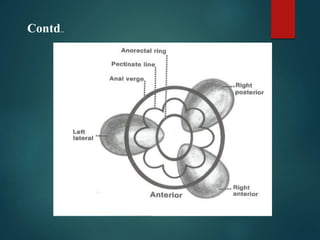
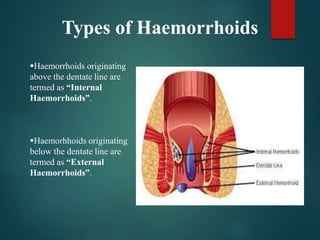
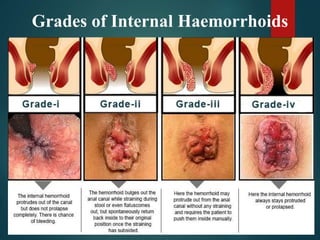
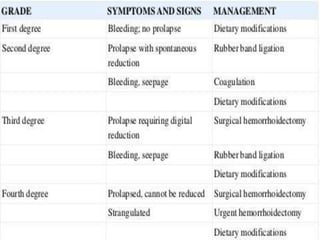
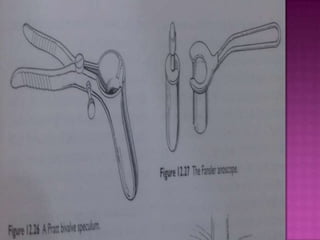
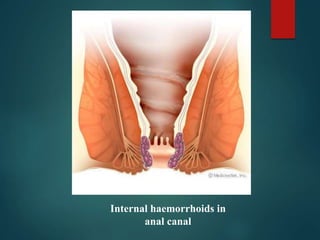
2. There are four grades of internal haemorrhoids based on the degree of prolapse. Symptoms include rectal bleeding, pain, itching, and swelling. Diagnosis involves examination and sometimes proctoscopy.
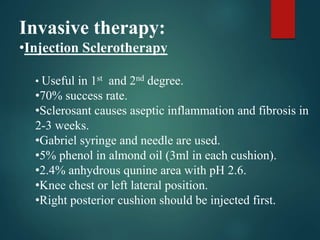
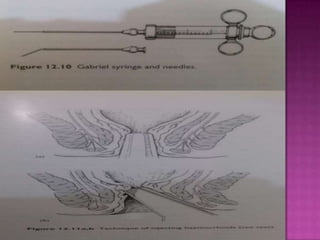
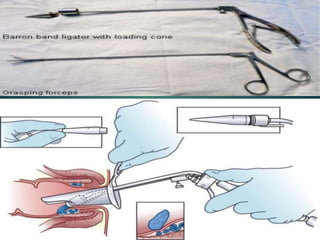
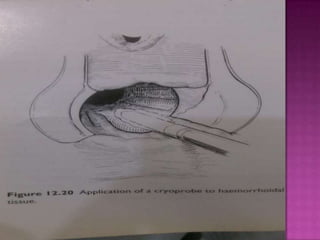
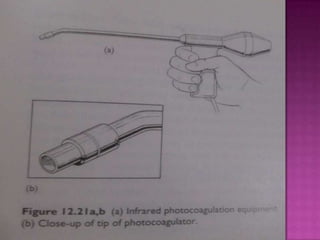
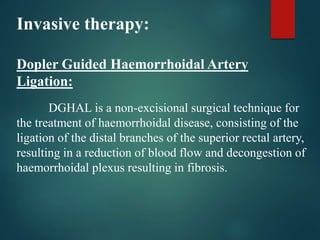
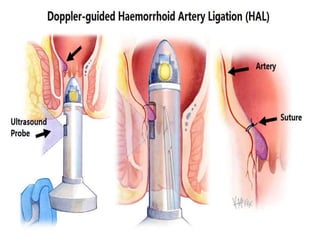
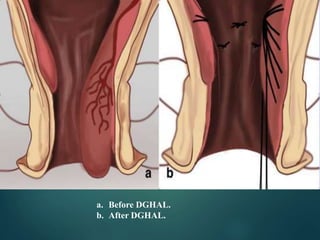
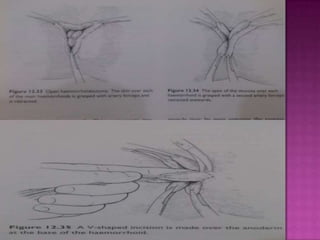
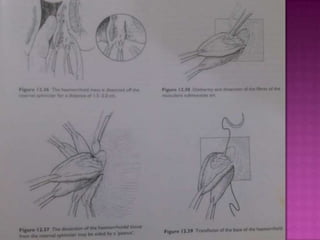
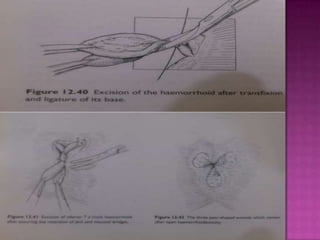
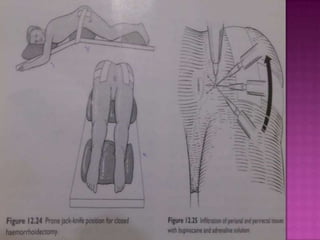
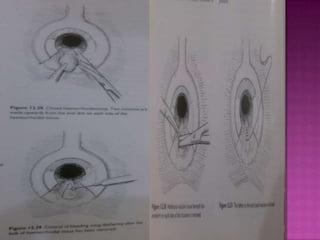
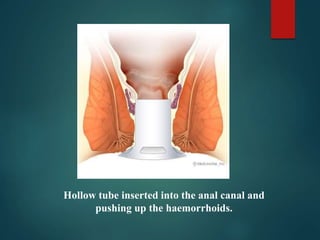
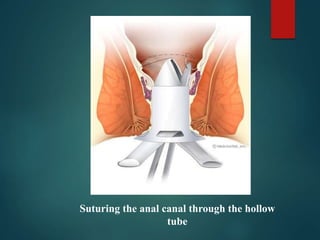
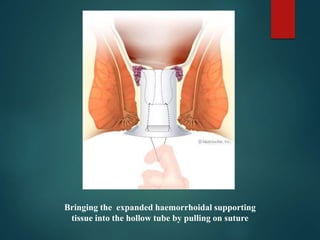
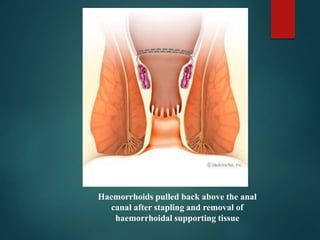
3. Treatment options range from conservative measures like diet changes to invasive procedures like rubber band ligation, injection sclerotherapy, and various surgical haemorrhoidectomy