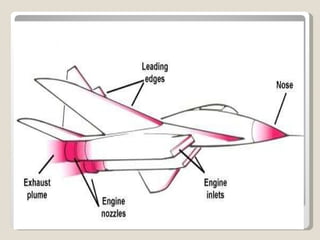
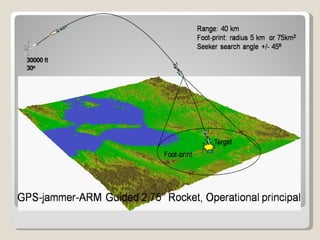
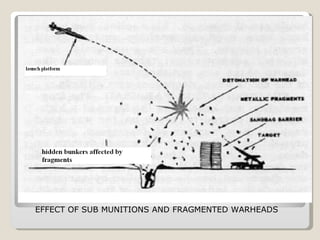
Guided missiles have evolved significantly over time and now play a major role in modern warfare. They can be guided through various technologies including laser, infrared, radar and GPS systems to precisely target enemies. Future smart weapons are anticipated to have greater autonomy, using advanced sensors and software to identify and engage threats on their own.