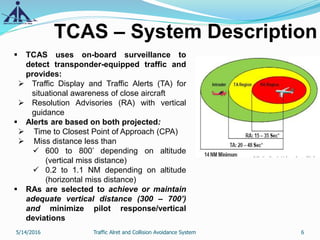
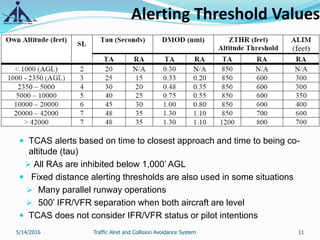
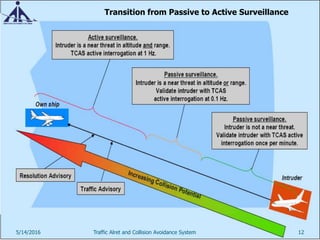
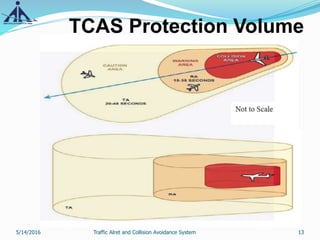
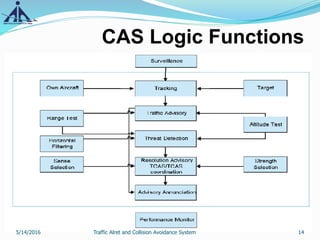
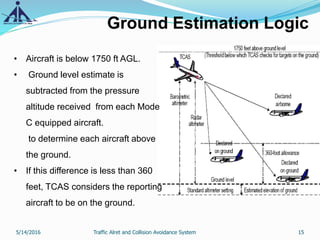
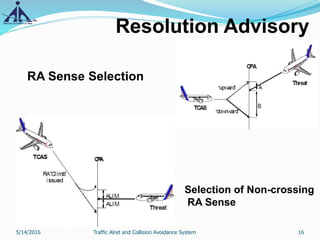
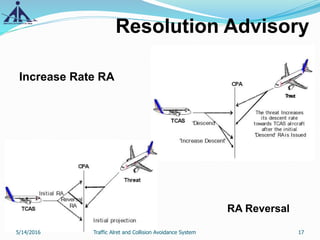
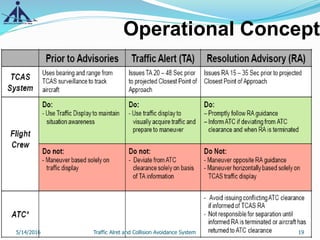
This document provides an overview of the Traffic Alert and Collision Avoidance System (TCAS). It discusses the history of TCAS, which began development in the 1970s following several mid-air collisions. It then describes the components and functions of TCAS, including how it detects intruder aircraft, issues traffic advisories and resolution advisories, and uses specific symbology in its displays. The document also outlines pilots' and air traffic controllers' responsibilities during TCAS advisories to maintain safety. In summary, TCAS is an airborne collision avoidance system that monitors nearby aircraft and issues alerts to pilots if there is a potential collision threat.