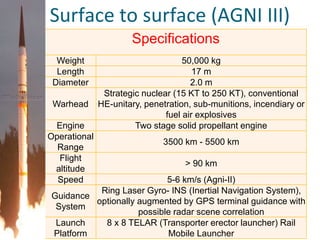
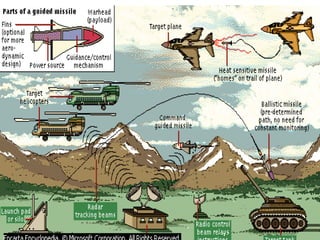
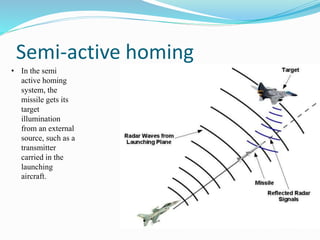
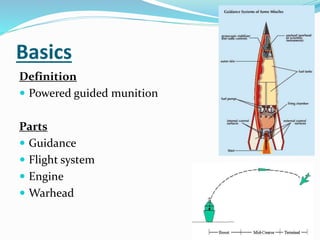
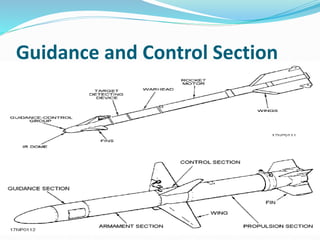
The document discusses missile technology, providing definitions and describing the basic parts of missiles including guidance, flight systems, engines, and warheads. It explains the principles of tracking, guidance, and flight for different types of missile engines. The document also describes different types of missiles and their specifications, including air-to-air, air-to-ground, surface-to-air, and ballistic missiles. It discusses various guidance systems used in missiles like inertial navigation systems, terrain contour matching, and global positioning satellites. Active homing, passive homing and semi-active homing guidance methods are also summarized.



![Air to air
Type Air to Air Missile
Place of origin India
Production history
Manufacturer DRDO
Produced Pre Production/Testing [1]
Specifications
Weight 154 kg
Length 3570 mm
Diameter 178 mm
Warhead
15 kg (33 lb) HE fragmentation
directional warhead
Detonation
mechanism
Radar proximity fuze
Engine Solid Fuel Rocket
Wingspan 254 mm
Operational
range
80-110 km[2][3]
Flight ceiling 66,000 ft
Speed Mach 4 + (4780 Km/h)
Guidance
system
Inertial, mid-course update and
terminal active radar homing (15 km)
Launch
platform
Su-30MKI,
HAL Tejas,
PAK FA / Sukhoi/HAL FGFA,
Mirage 2000 and
Mig-29.
(Astra)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/missiletechnology-150102022802-conversion-gate02/85/Missile-technology-7-320.jpg)