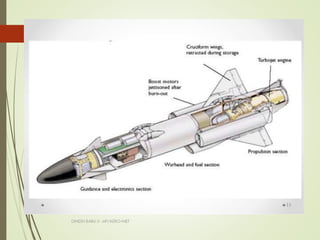
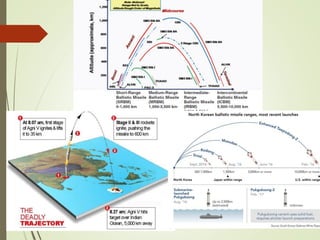
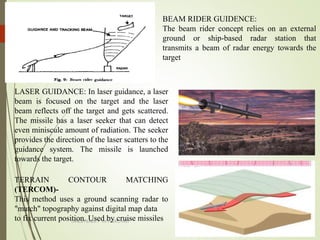
Missiles are classified based on their type, launch mode, range, propulsion, warhead, and guidance system. The document outlines the key classifications of each category: types include cruise and ballistic missiles; launch modes include surface-to-surface, surface-to-air, etc.; ranges are short, medium, intermediate, and intercontinental; propulsion includes solid, liquid, hybrid, ramjet, scramjet, and cryogenic; warheads can be conventional, strategic, chemical, biological, or nuclear; and guidance systems range from wire guidance to inertial guidance, terrain comparison, and laser or GPS guidance.