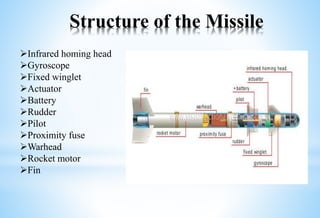
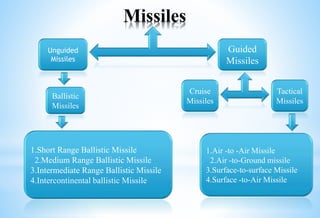
Pakistan has developed an advanced missile program. It has short-range missiles like Ghaznavi (300km) and Shaheen-I (750-900km), and medium-range missiles like Ghauri-I (1,500km) and Shaheen-III (2,750km). Pakistan also has the tactical Nasr missile (60km) and the cruise missile Babur (450+km). Missiles work using rocket propulsion and guidance systems, and can have different payloads like conventional, chemical, biological or nuclear warheads. Pakistan's missiles demonstrate its growing indigenous defense capabilities.