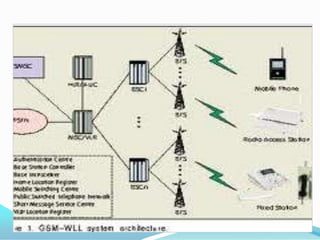
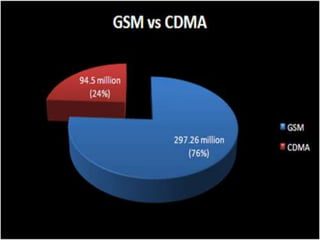
There are two main cellular network technologies: GSM and CDMA. GSM carriers include Cingular Wireless, T-Mobile, and others, while CDMA carriers include Sprint PCS and Verizon. Understanding the differences between GSM and CDMA, such as coverage, data speeds, roaming capabilities, and use of SIM cards, can help a customer choose the preferable network for their needs. While CDMA was initially faster, both technologies continue advancing and neither is clearly superior.