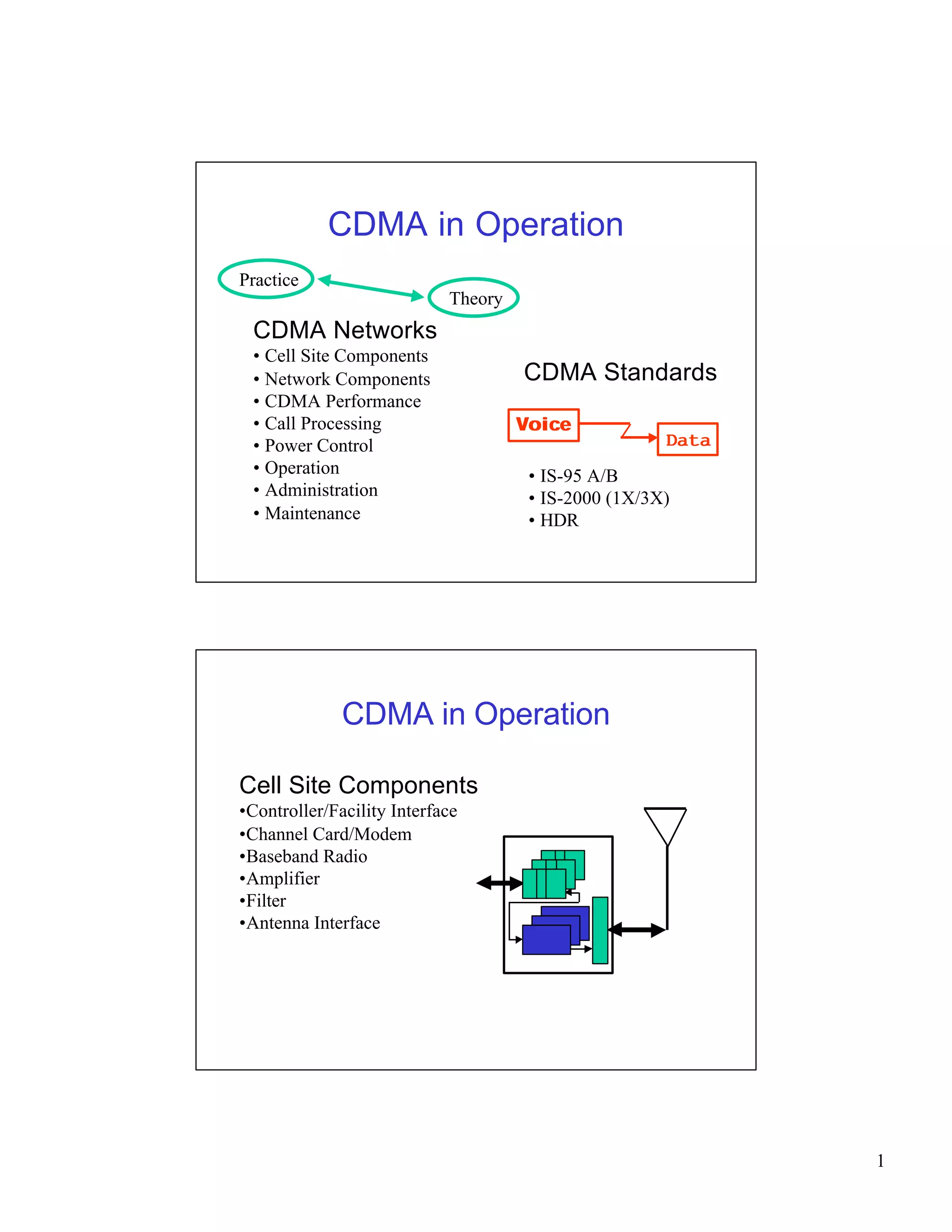
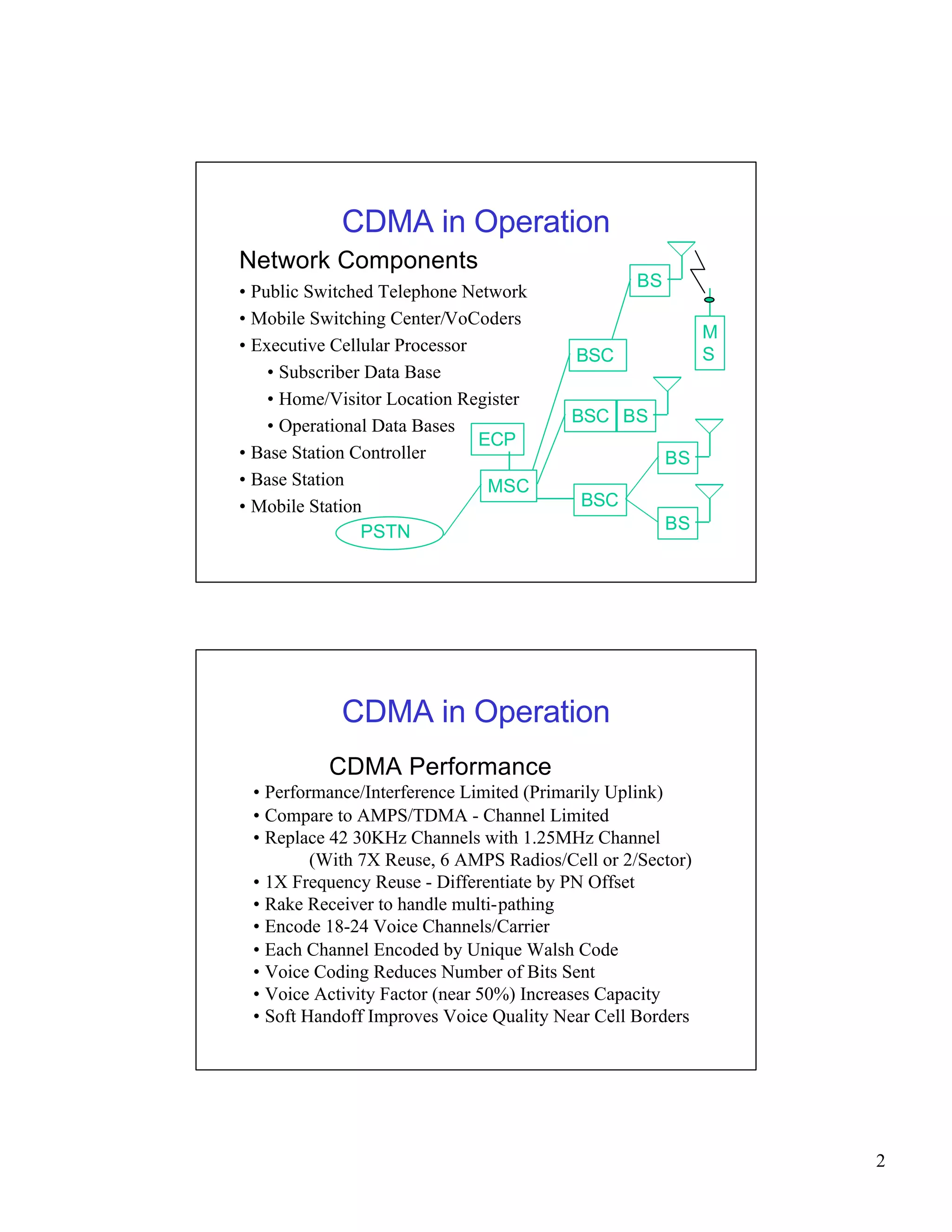
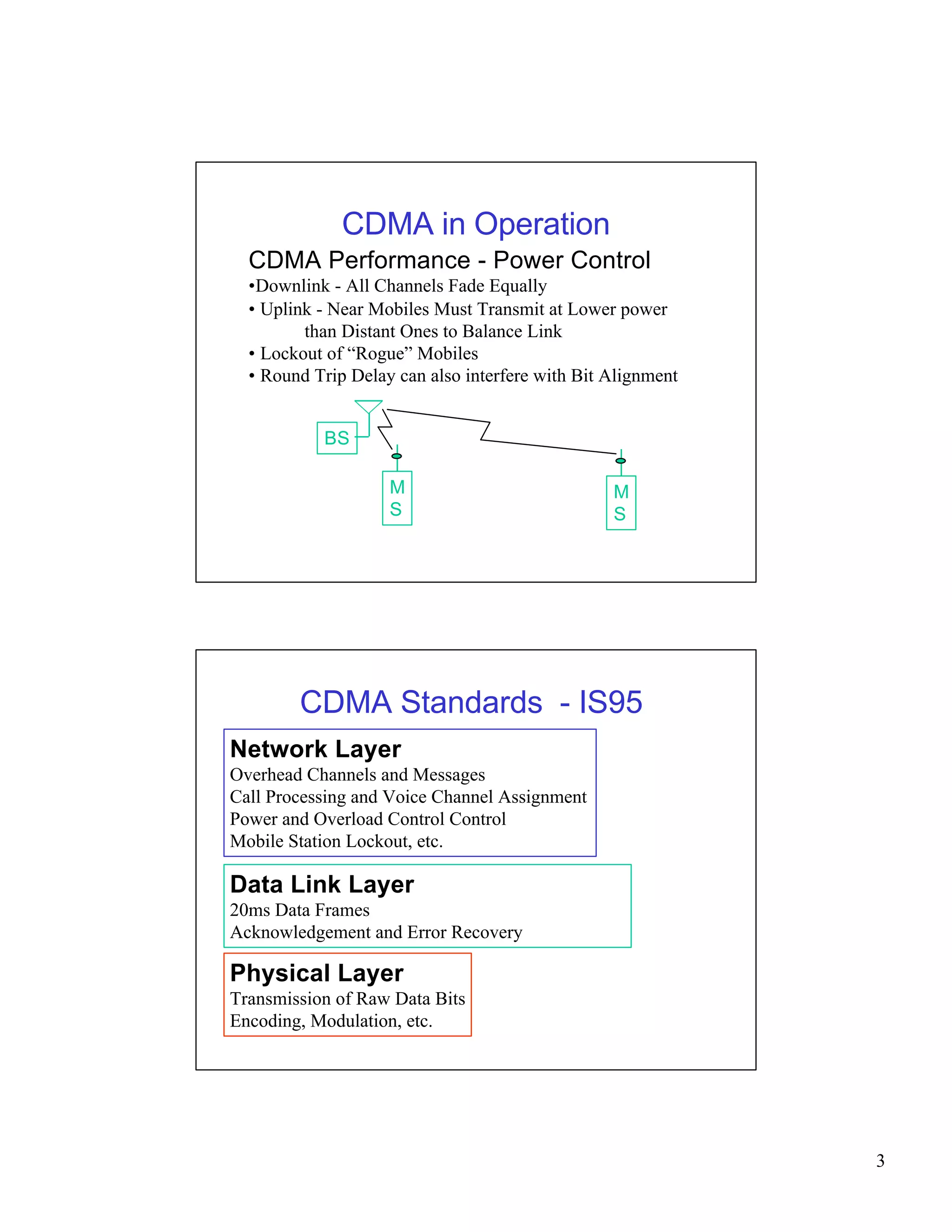
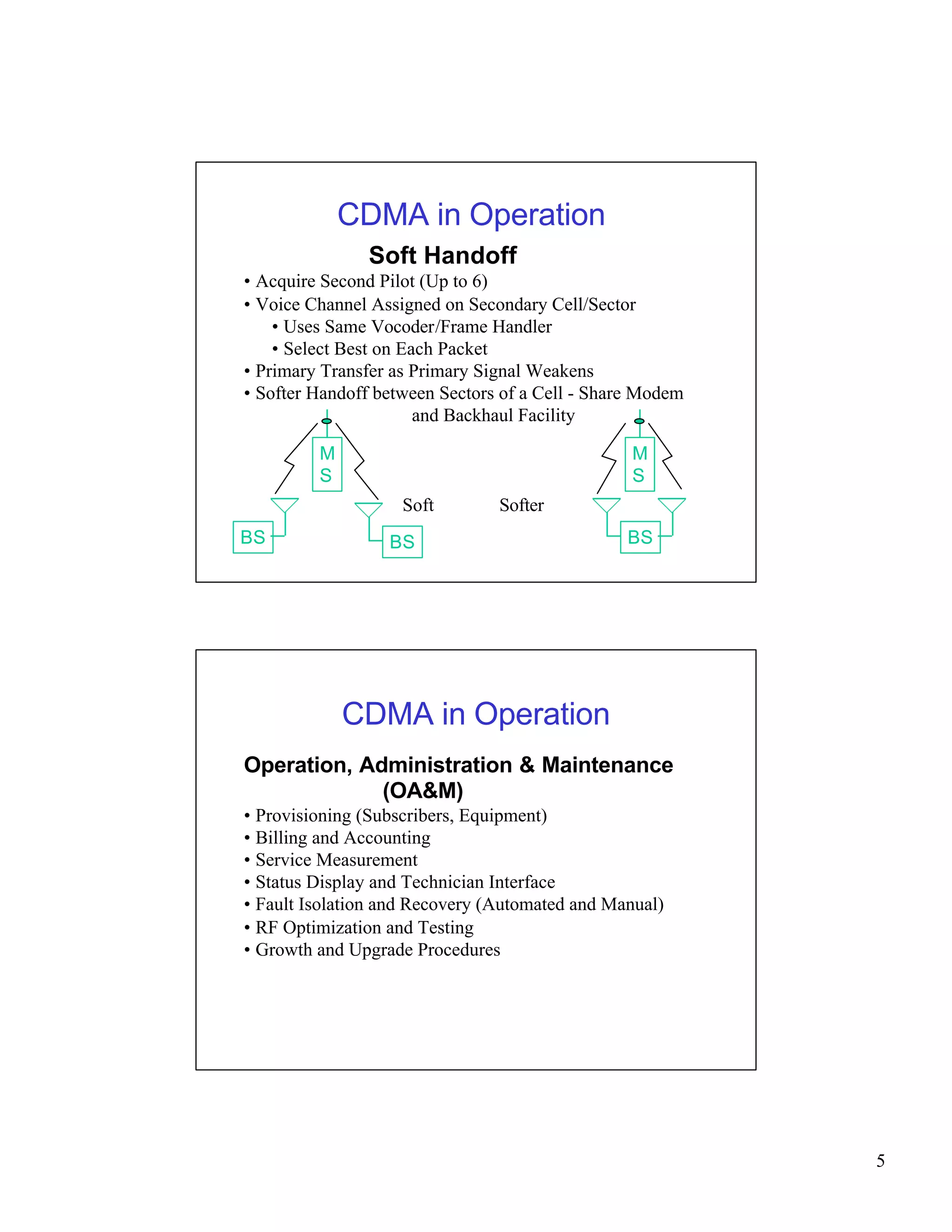
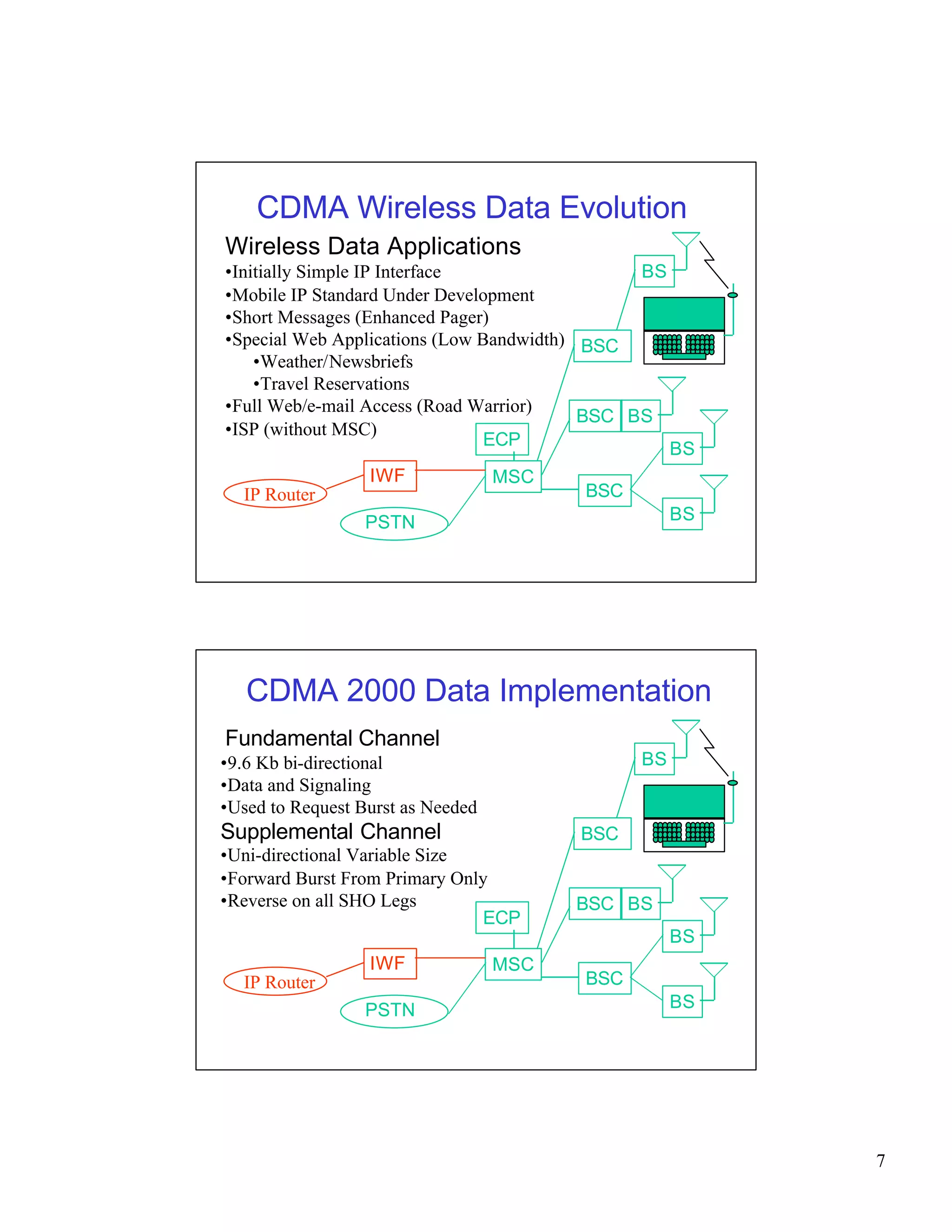
CDMA networks allow multiple users to share the same frequency band by differentiating users with codes. The document discusses the components of CDMA networks including cell sites, switching centers, and standards. It describes how CDMA handles call processing, power control, and soft handoffs to maintain quality of service as users move between different areas of coverage. The evolution of CDMA technology for voice and data services is also summarized.