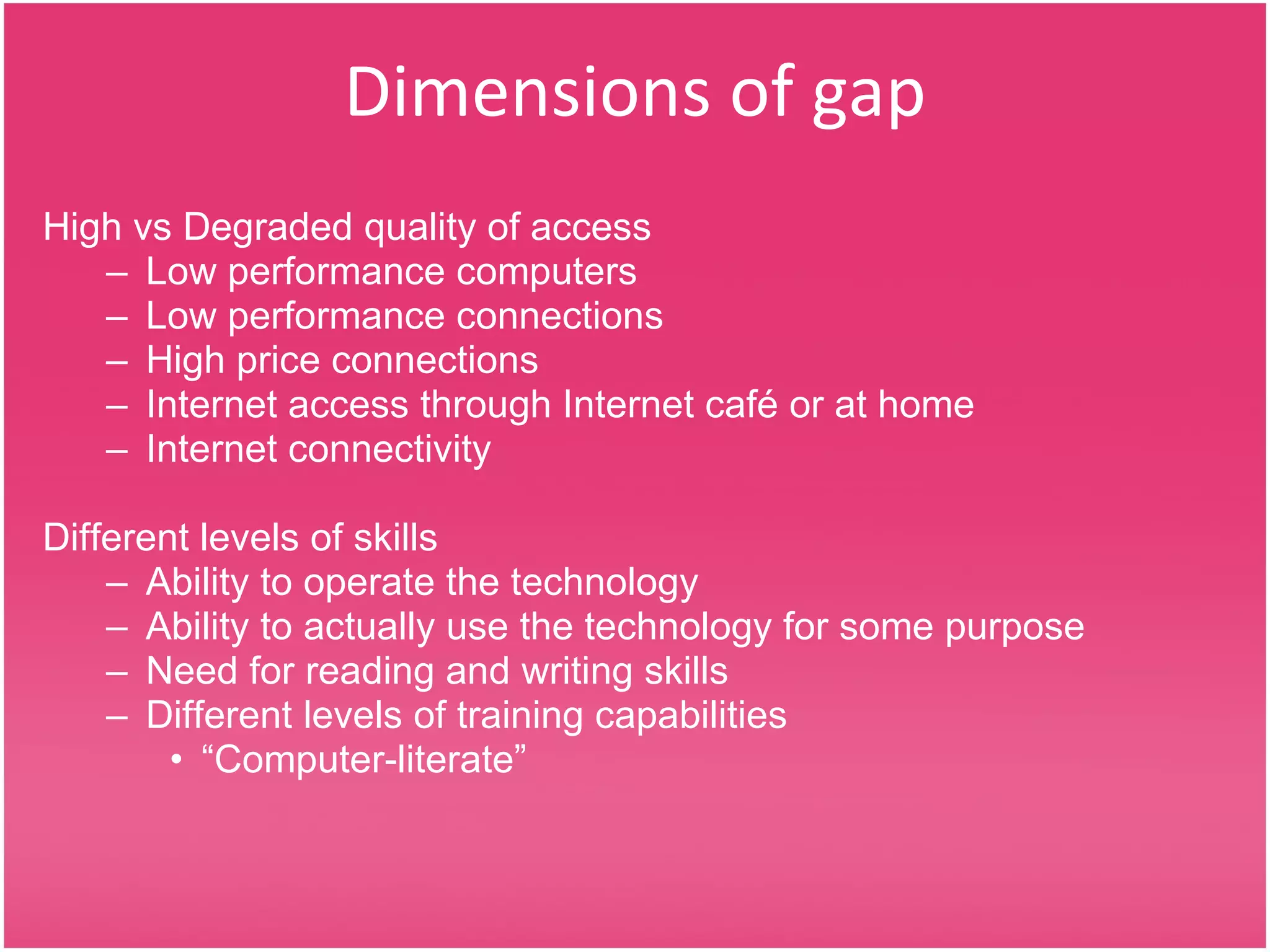
The document defines key terms related to information and communication technology (ICT) and the digital divide. It discusses debates around prioritizing ICT development, both criticisms and arguments in support. United Nations Millennium Development Goals related to ICT access are outlined. The document explores how ICTs can support education, health, small and medium enterprises, and governance. It analyzes dimensions of the digital divide and importance of closing the gap, proposing strategies to increase access and relevance of ICTs.