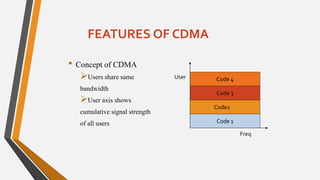
This document compares GSM and CDMA mobile technologies. It outlines that GSM uses TDMA and FDMA to allow multiple users to access frequencies, while CDMA uses direct sequence spread spectrum and unique codes to separate users on the same frequency. The document discusses features of each technology such as frequency reuse in GSM. It analyzes advantages of both such as better voice quality in CDMA due to use of entire spectrum, and international roaming capability in GSM. Overall, the document provides a technical overview comparing key aspects of GSM and CDMA mobile networks.