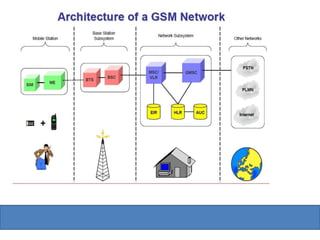
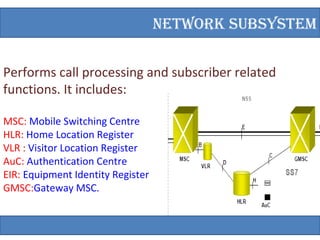
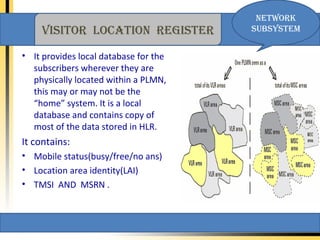
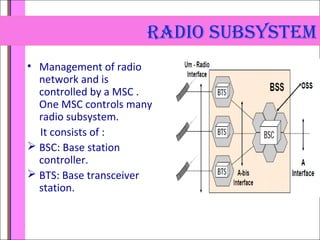
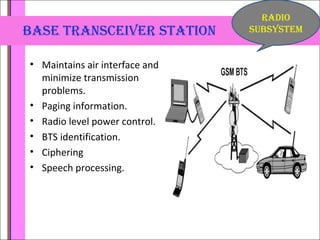
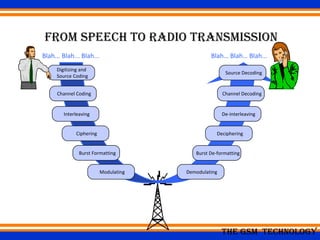
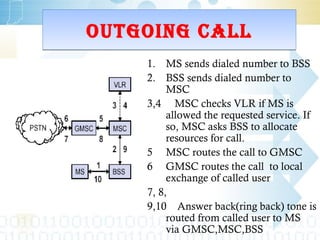
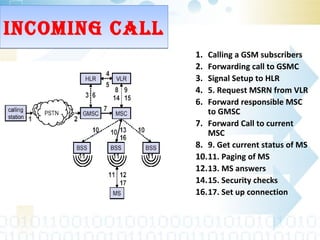
Global System for Mobile (GSM) is a second generation cellular standard developed for voice services and data delivery using digital modulation. It has a network subsystem including components like the MSC, HLR, VLR, and AuC that handle call processing and subscriber information. The radio subsystem consists of BSCs controlling multiple BTSs to manage radio network access. GSM provides international roaming, high quality voice calls, and supports data services like SMS and fax in addition to voice.