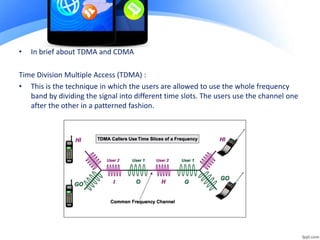
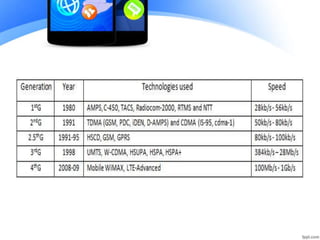
The document summarizes the evolution of mobile networks across five generations from 1G to 5G. 1G introduced analog cellular technology in the 1980s, while 2G brought digital networks and SMS. 2.5G and 3G provided improved data speeds up to 28 Mbps. 4G networks such as LTE use OFDMA and provide speeds up to 1 Gbps. 5G is the emerging generation that targets peak speeds of almost 1 Gbps for stationary devices and 100 Mbps for mobile. Each generation brought major technical advancements and higher speeds for improved user experiences.