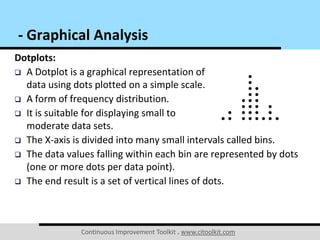
The document outlines a comprehensive continuous improvement toolkit that includes various graphical analysis tools for data collection and process evaluation, such as check sheets, flowcharts, and control charts. It emphasizes the importance of different graph types, such as line charts, pie charts, and scatter plots, for understanding data trends, relationships, and variations. Additionally, it provides examples and explanations of each graph type's appropriate use and interpretation to enhance decision-making and process improvement.