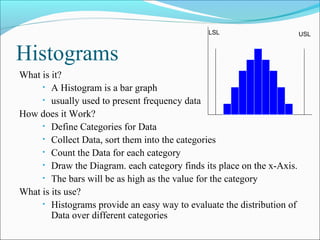
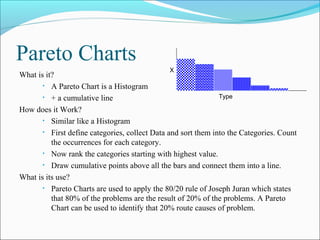
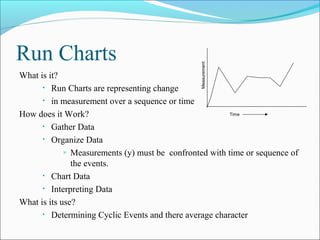
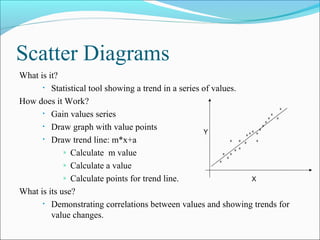
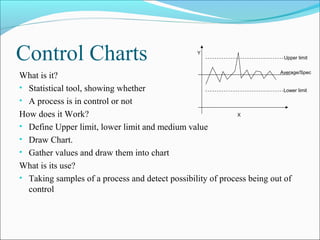
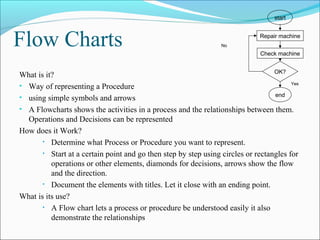
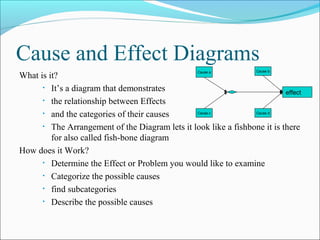
The document discusses 7 quality techniques: histograms, Pareto charts, run charts, scatter diagrams, control charts, flow charts, and cause-and-effect diagrams. It provides a definition and overview of how each technique works and its intended use. Histograms evaluate data distribution, Pareto charts identify the most common problems using the 80/20 rule, and run charts detect cyclic events. Scatter diagrams show trends in value changes, while control charts determine if a process is in or out of control. Flow charts map out processes and relationships, and cause-and-effect diagrams examine the causes behind an effect or problem.