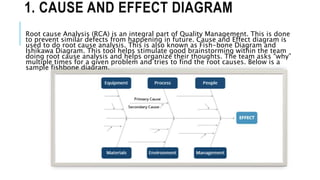
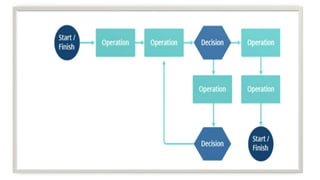
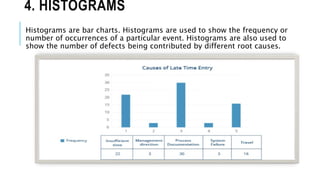
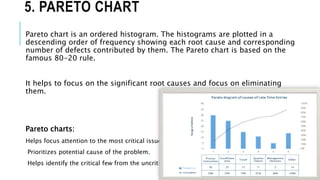
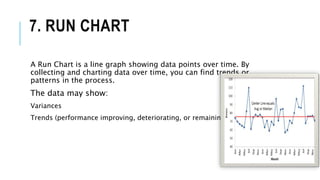
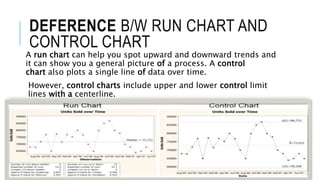
The document outlines various quality tools used in data analysis and quality management, emphasizing their importance for process compliance and continuous improvement. Key tools include cause and effect diagrams, flowcharts, control charts, histograms, Pareto charts, scatter diagrams, and run charts, each serving specific purposes in identifying and analyzing quality issues. These tools facilitate effective root cause analysis, process visualization, performance monitoring, and trend identification to enhance overall quality management.