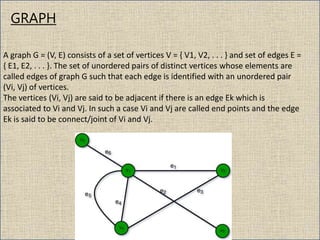
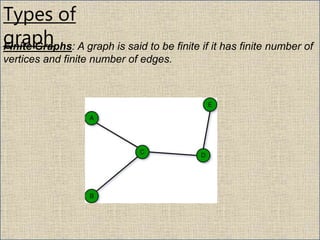
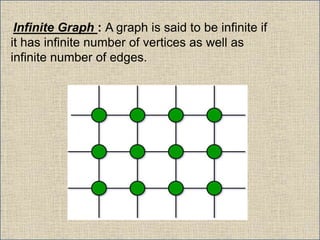
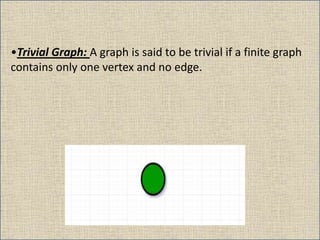
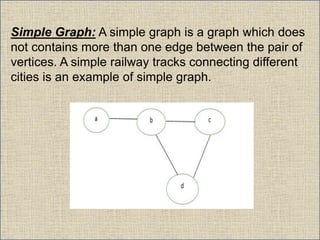
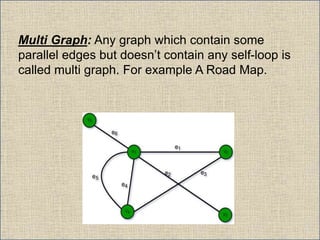
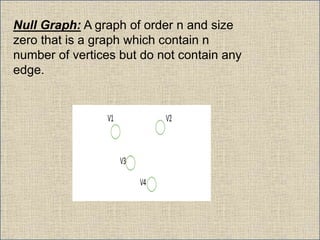
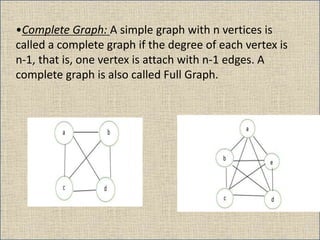
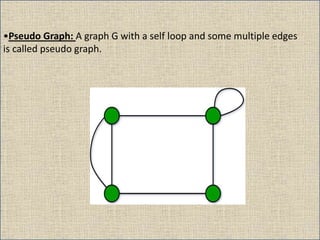
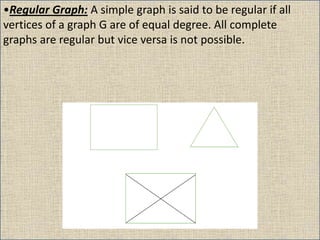
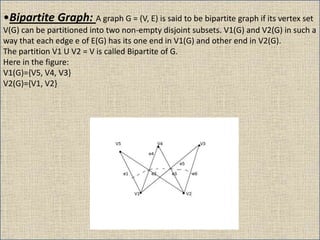
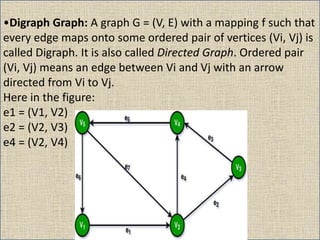
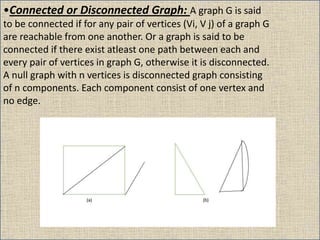
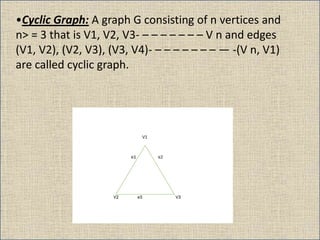
The document provides an overview of graph theory, detailing definitions and classifications of various types of graphs, including finite, infinite, trivial, simple, multi, complete, pseudo, regular, bipartite, directed (digraph), connected, disconnected, and cyclic graphs. It explains associated terms like vertices, edges, and adjacency, along with examples for better understanding. Each type of graph is characterized by specific properties related to the arrangement and connectivity of its vertices and edges.