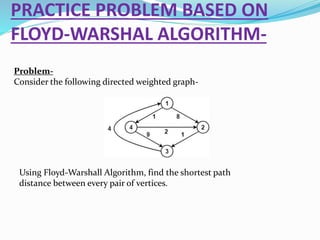
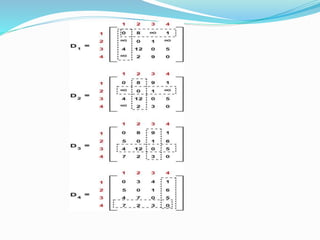
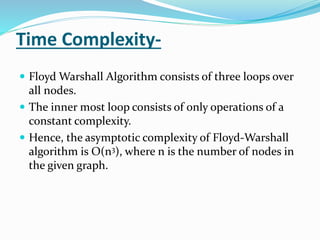
The document presents an overview of Floyd-Warshall algorithm, which is used to solve the all pairs shortest path problem in weighted directed graphs. It explains the algorithm's implementation, advantages, and time complexity, emphasizing its suitability for dense graphs. A practice problem is included to illustrate the algorithm's application step-by-step.





![ALGORITHM
Create a |V| x |V| matrix, M, that will describe the distances
between vertices
For each cell (i,j) in M do-
if i = = j
M[ i ][ j ] = 0 // For all diagonal elements, value = 0
if (i , j) is an edge in E
M[ i ][ j ] = weight(i,j) // If there exists a direct edge
between the vertices, value = weight of edge
else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floyd-1-230616071143-d2dadaed/85/Floyd-s-and-Warshal-s-Algorithm-ujjwal-matoliya-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![ M[ i ][ j ] = infinity // If there is no direct edge
between the vertices, value = ∞
for k from 1 to |V|
for i from 1 to |V|
for j from 1 to |V|
if M[ i ][ j ] > M[ i ][ k ] + M[ k ][ j ]
M[ i ][ j ] = M[ i ][ k ] + M[ k ][ j ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floyd-1-230616071143-d2dadaed/85/Floyd-s-and-Warshal-s-Algorithm-ujjwal-matoliya-pptx-7-320.jpg)