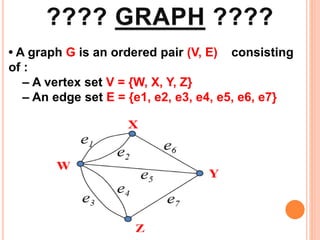
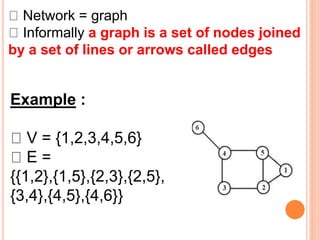
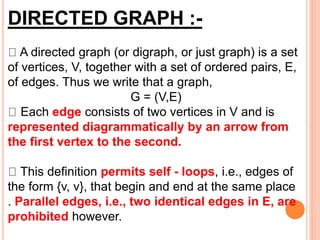
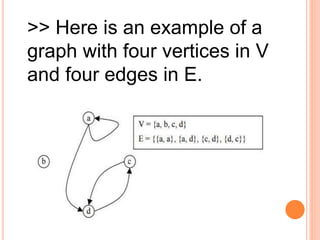
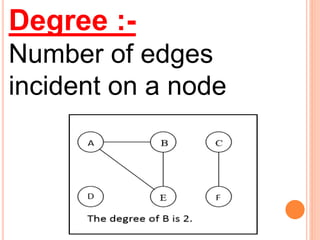
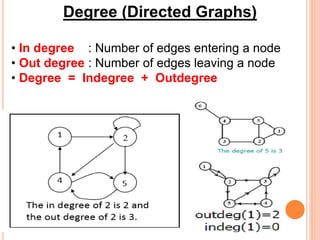
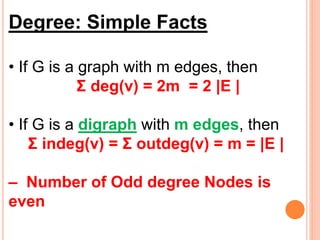
This document defines and provides examples of different types of graphs and digraphs. It defines a graph as an ordered pair of vertices and edges, and defines a digraph as a graph where edges have a direction from one vertex to another. It provides examples of simple, symmetric, asymmetric, complete, and balanced digraphs. It also defines in-degree, out-degree, and total degree of vertices in digraphs.