This document provides an overview of syntax-directed translation and attribute grammars. It discusses:
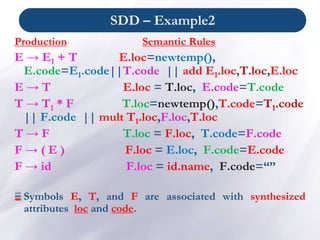
- Syntax-directed definitions associate semantic rules with production rules to evaluate attributes and perform actions like code generation. Attributes can represent various types of information.
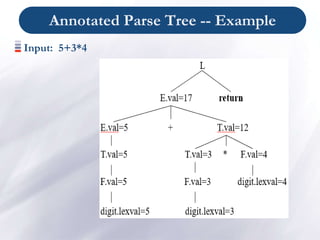
- Syntax trees can be annotated with attribute values. The order attributes are computed depends on semantic rule dependencies.
- Translation schemes specify an order for evaluating semantic actions associated with productions. This provides implementation details omitted from syntax-directed definitions.
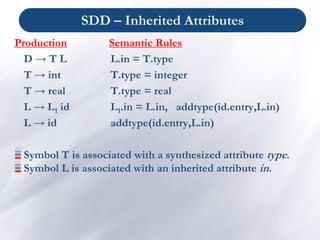
- S-attributed and L-attributed definitions are subclasses that allow efficient single-pass evaluation during parsing by restricting how attributes can be used.











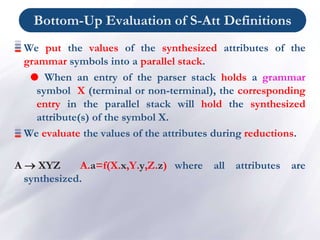

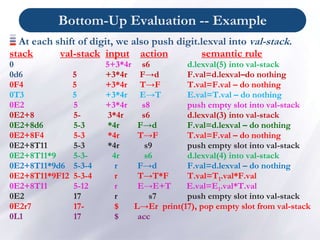
![Bottom-Up Eval. of S-Att Definitions (Cont.)
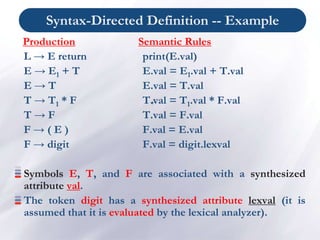
Production Semantic Rules
L → E return print(val[top-1])
E → E1 + T val[ntop] = val[top-2] + val[top]
E → T
T → T1 * F val[ntop] = val[top-2] * val[top]
T → F
F → ( E ) val[ntop] = val[top-1]
F → digit
At each shift of digit, we also push digit.lexval into val-
stack.
At all other shifts, we do not put anything into val-stack
because other terminals do not have attributes (but we
increment the stack pointer for val-stack).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-syntaxdirectedtranslation-copy-230417230521-c2d2881e/85/Chapter-5-Syntax-Directed-Translation-Copy-ppt-20-320.jpg)