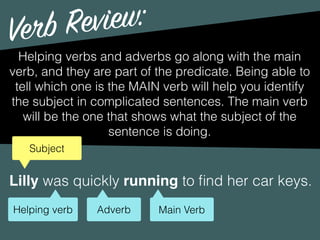
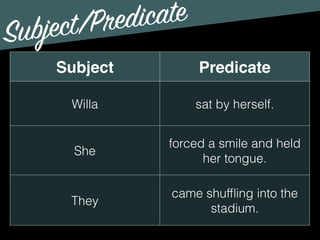
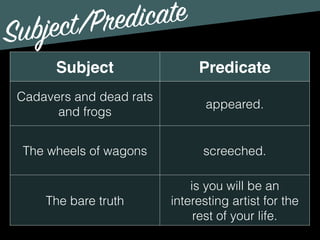
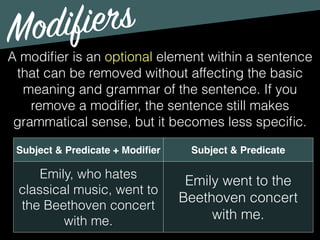
The document discusses the key components of sentences: subjects, predicates, and modifiers. It defines subjects as the who or what in a sentence, and predicates as the part that tells something about the subject. Every sentence must have both a subject and a predicate. It also discusses verbs, subjects, compound subjects/predicates, and modifiers. Modifiers are optional elements that can be removed without changing the basic meaning of the sentence.