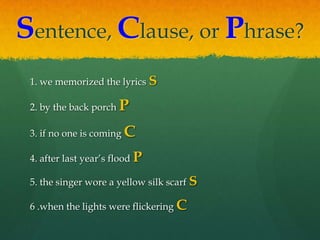
The document defines and provides examples of clauses, phrases, and sentences. It explains that a clause contains both a subject and a verb, while a phrase does not. An independent clause conveys a complete thought on its own, while a subordinate clause does not. Examples are given of independent and subordinate clauses as well as phrases. Readers are then asked to identify groups of words as sentences, clauses, or phrases. The document concludes by explaining how subordinate clauses must be combined with independent clauses to form complete sentences.