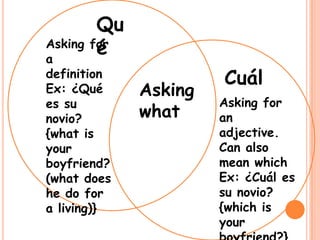
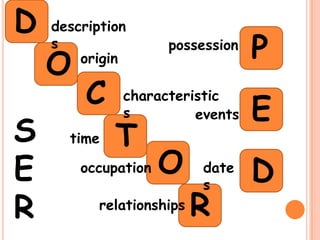
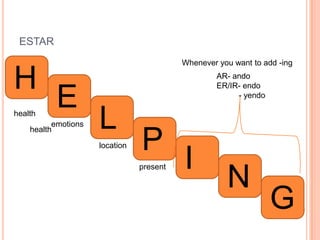
The document provides a table of contents for a Spanish grammar book. It lists and defines various Spanish grammar topics like verbs tenses (preterite, imperfect), commands, transitions words, verbs like gustar, reflexive verbs, and ser vs estar among others. It also provides examples and conjugations for many of the grammar points.