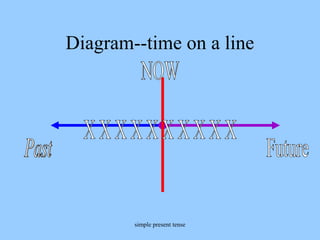
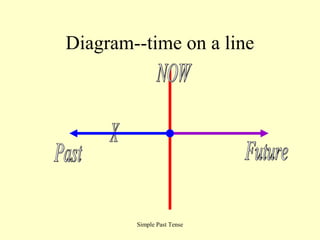
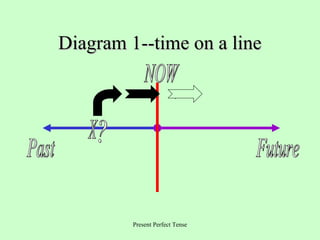
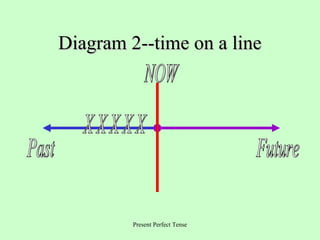
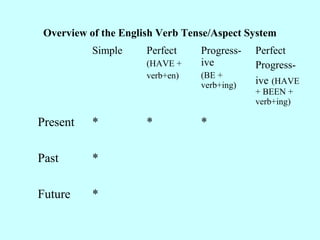
This document provides an overview of English verb tenses and their uses. It discusses the simple present, past, and future tenses. It also covers the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect tenses. Additionally, it explains the present progressive, past progressive, and future progressive tenses. Finally, it discusses combinations of tenses like the present perfect progressive and future perfect progressive. Examples and forms are provided for each tense.