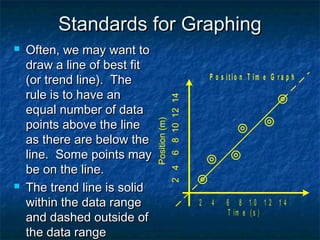
This document discusses standards for graphing data from scientific experiments. It explains that the independent variable is plotted horizontally and the dependent variable vertically. All graphs must be clearly labeled with units and titles. Data points should be circled to indicate possible error. A line of best fit can be drawn to represent the overall trend, ignoring individual error. The area under a velocity-time graph represents displacement. Graphing data allows relationships between variables to be identified and communicated.