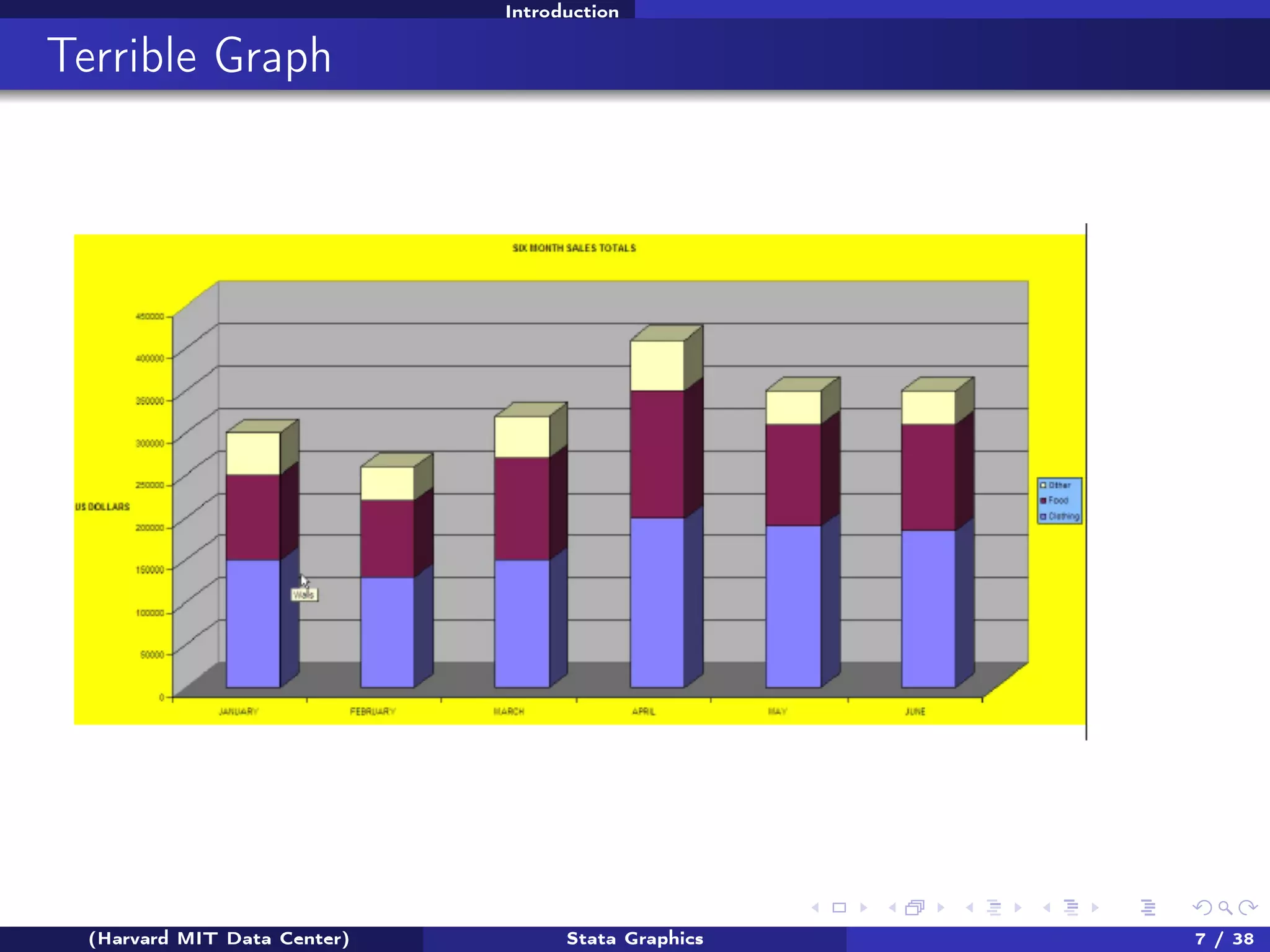
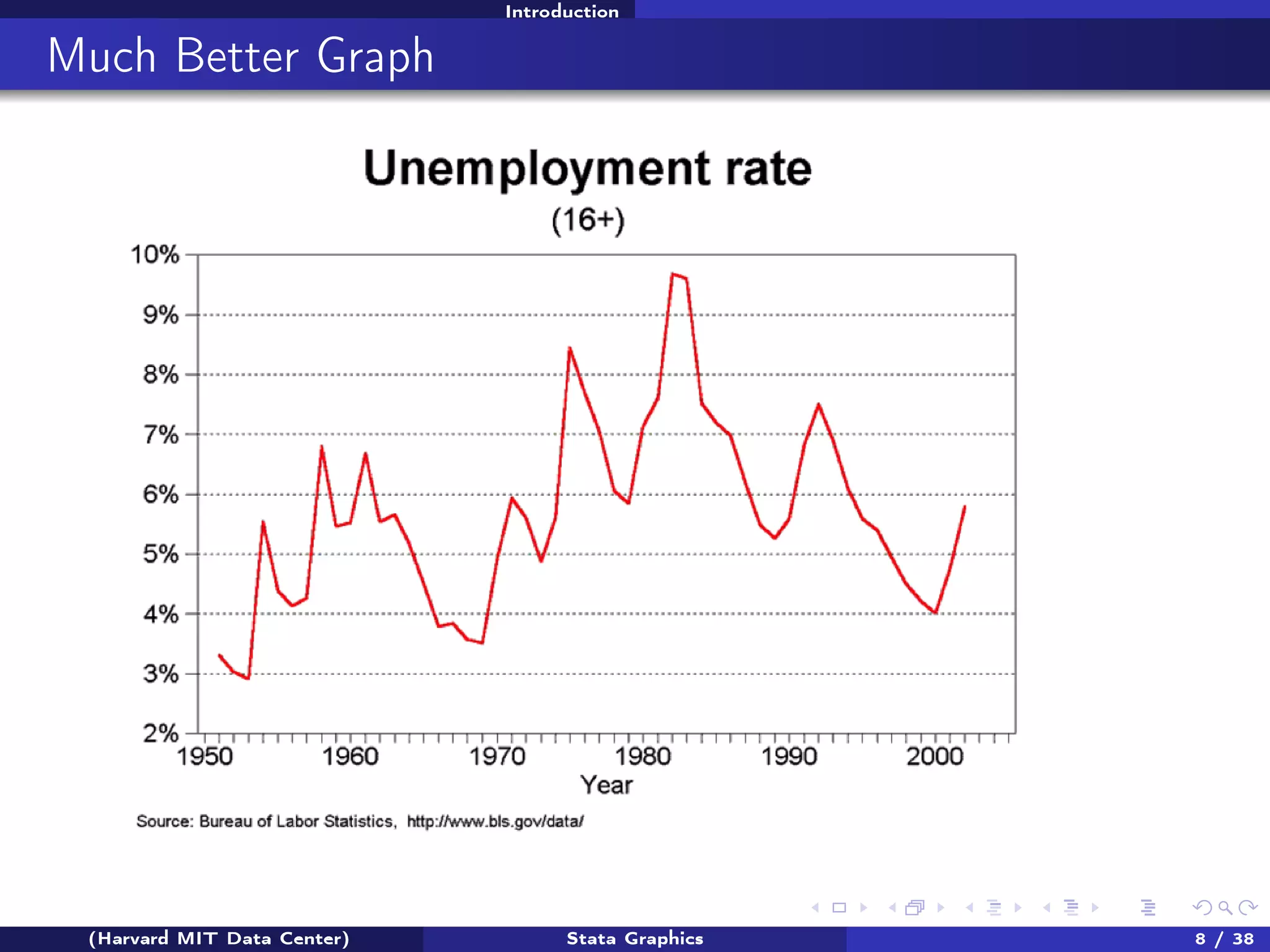
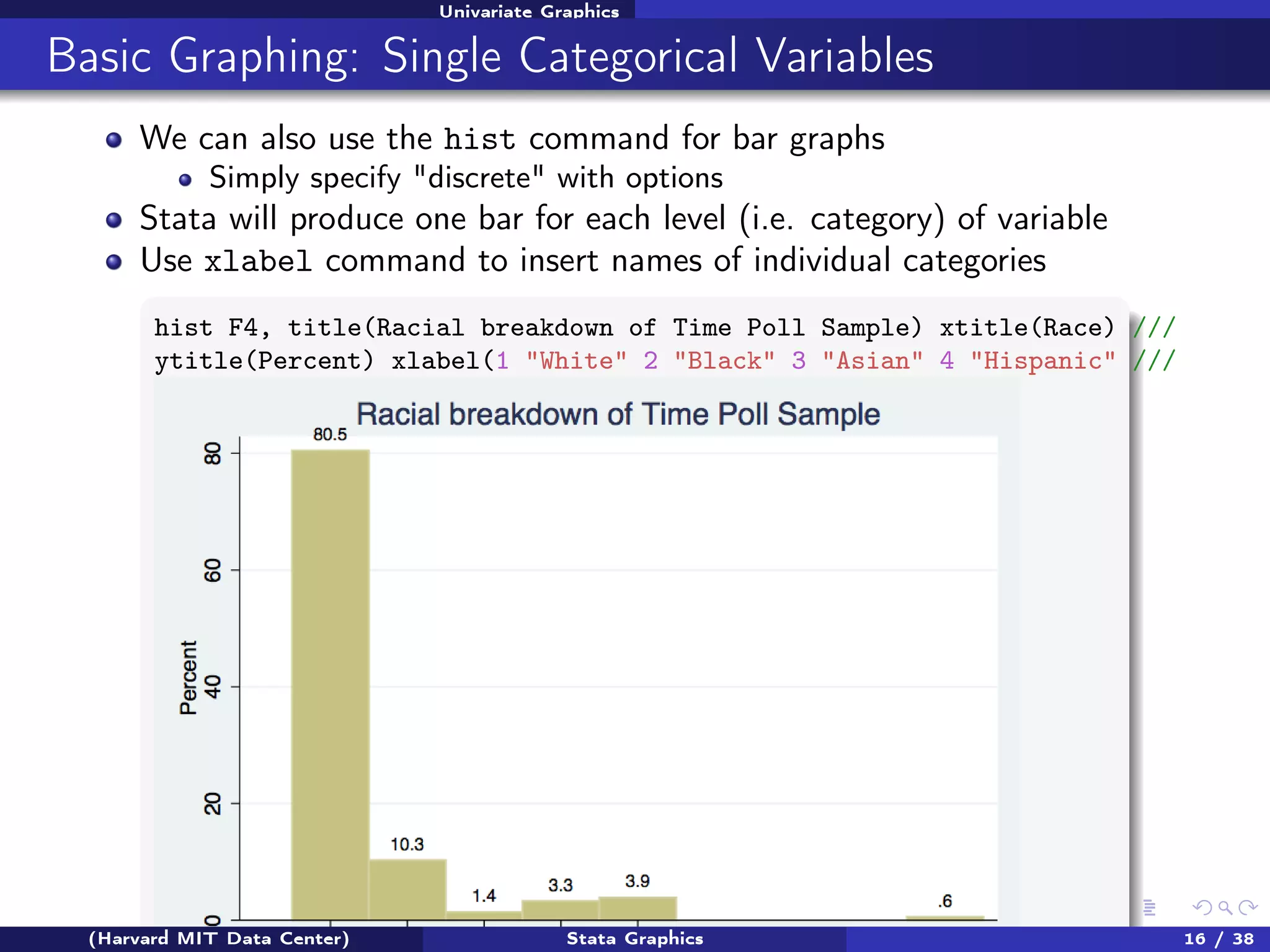
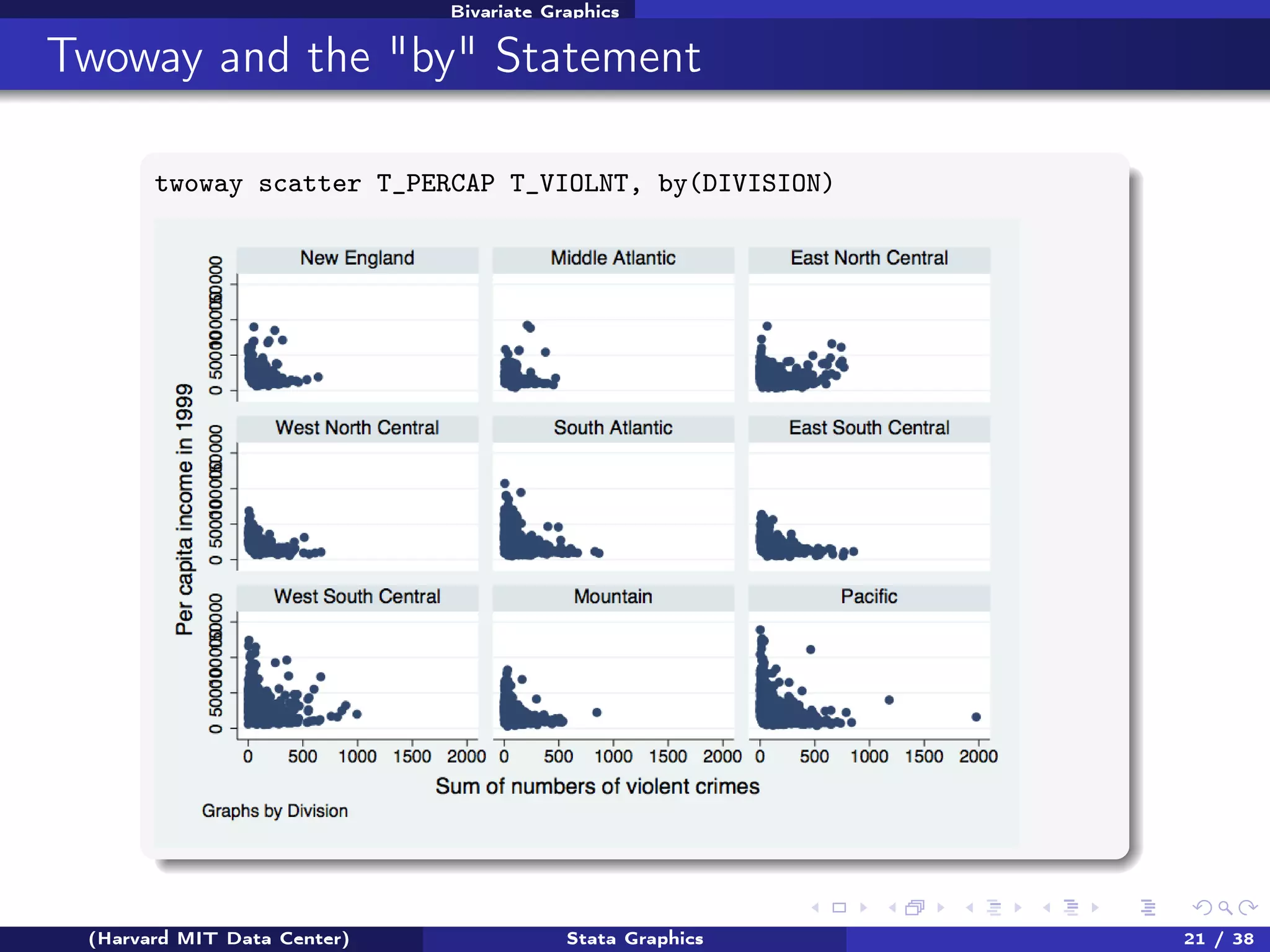
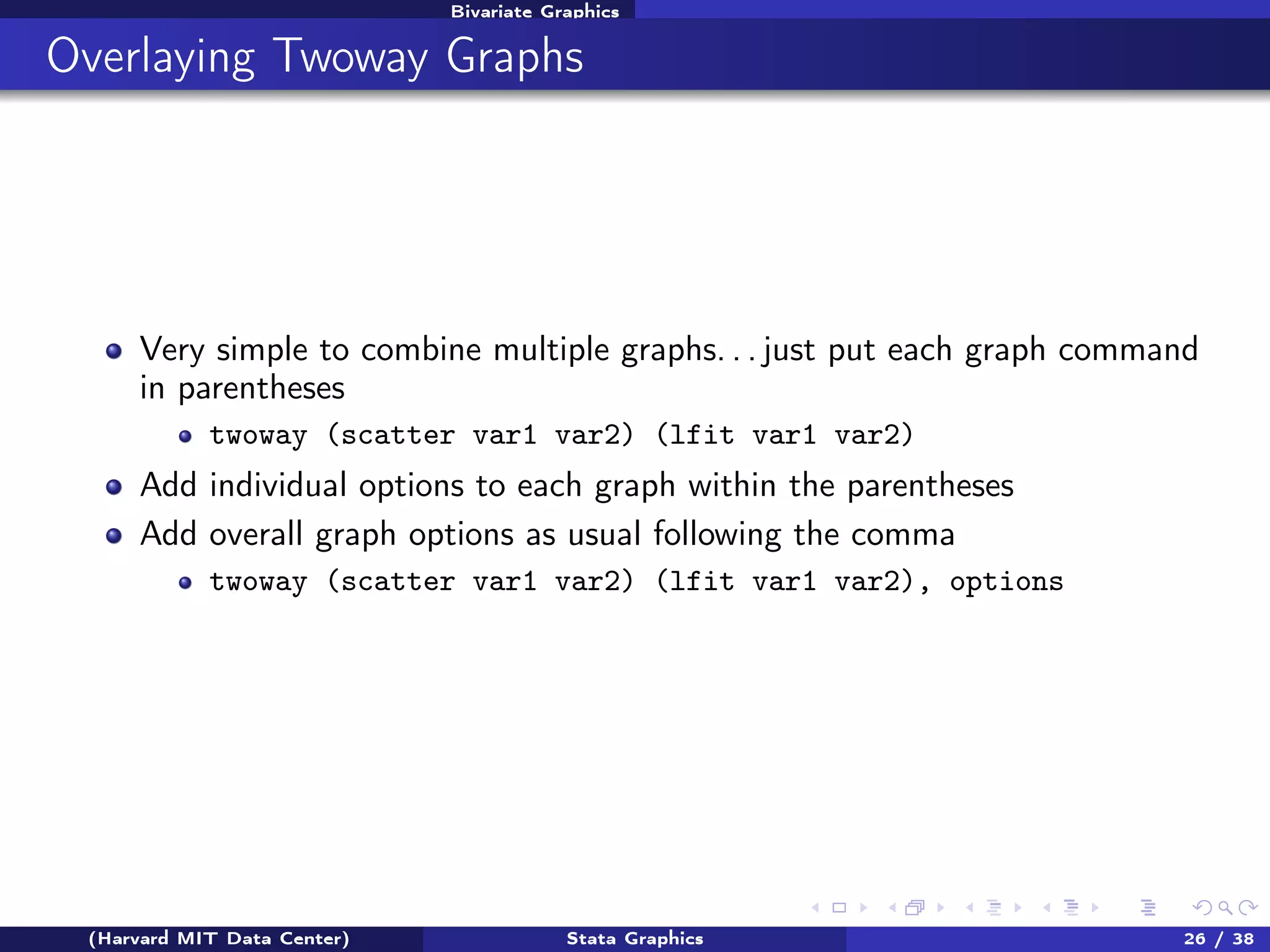
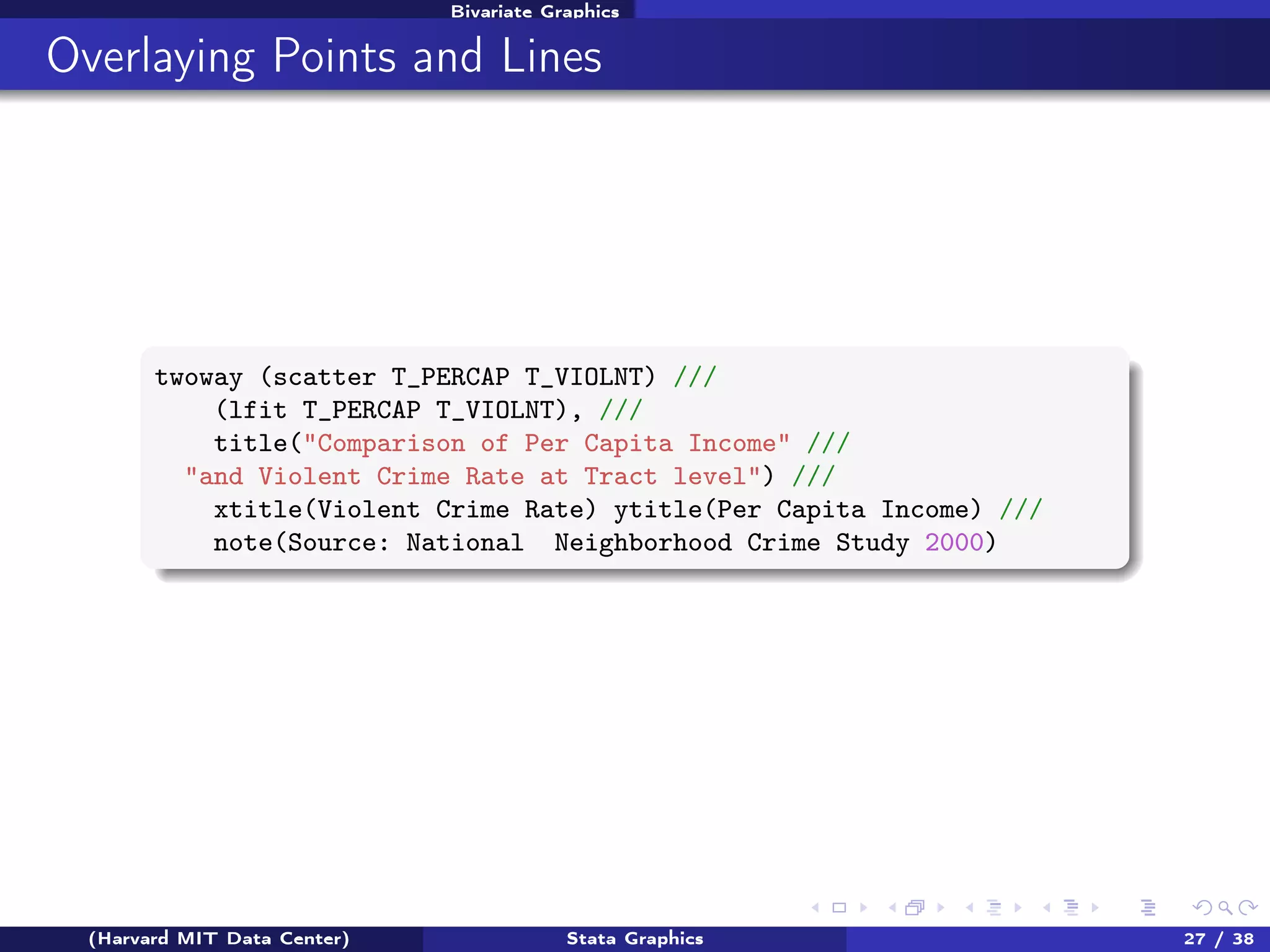
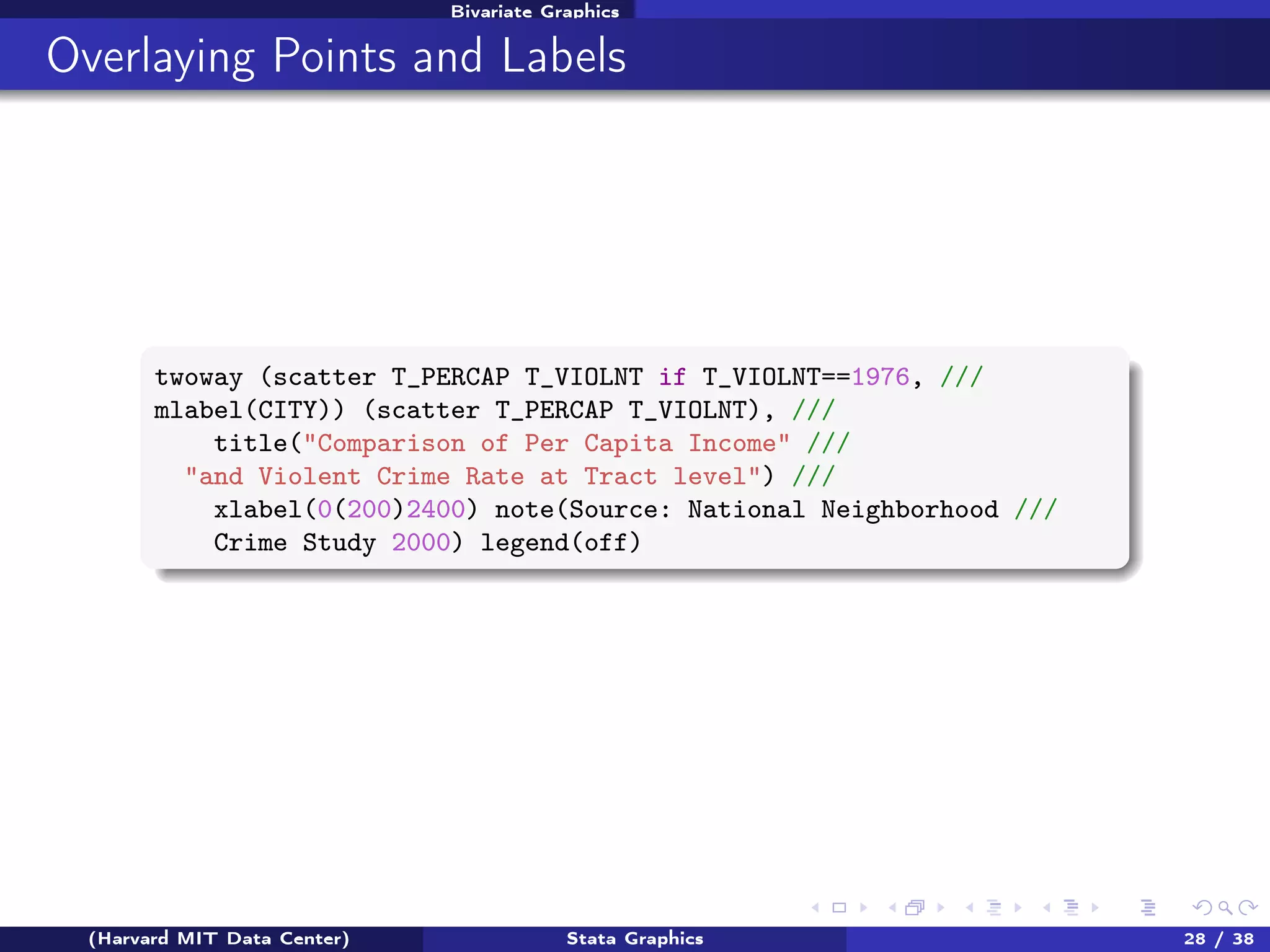
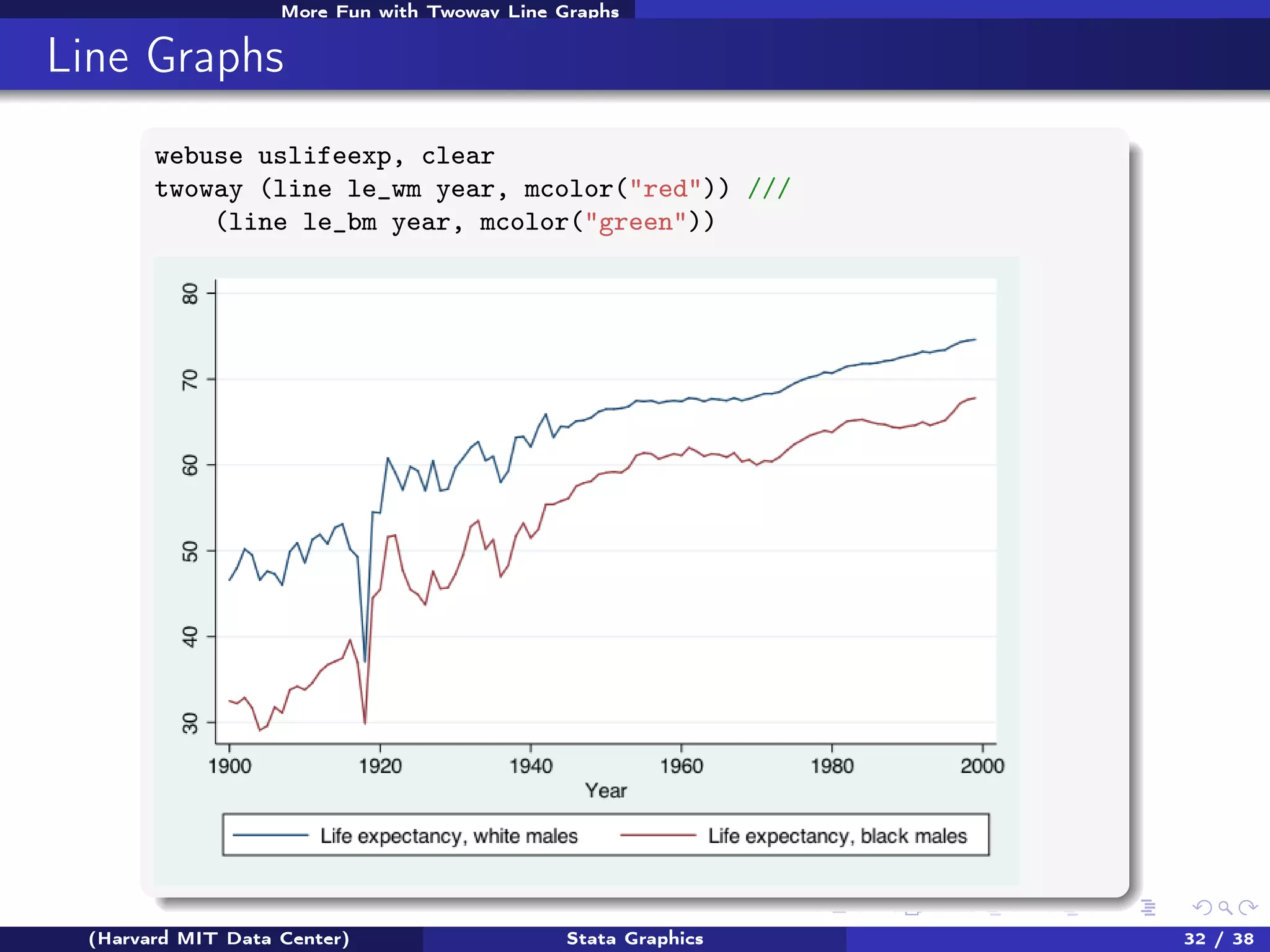
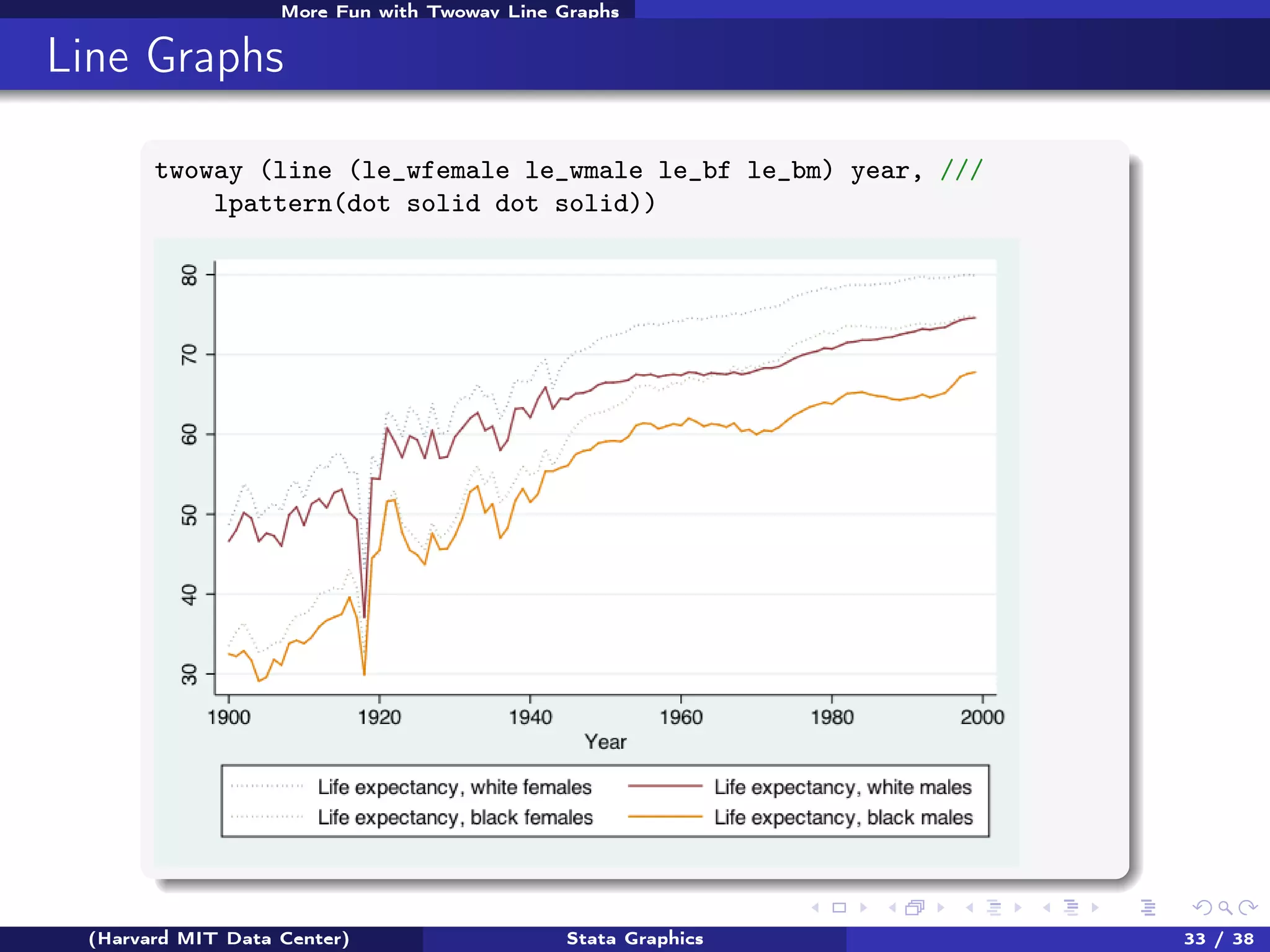
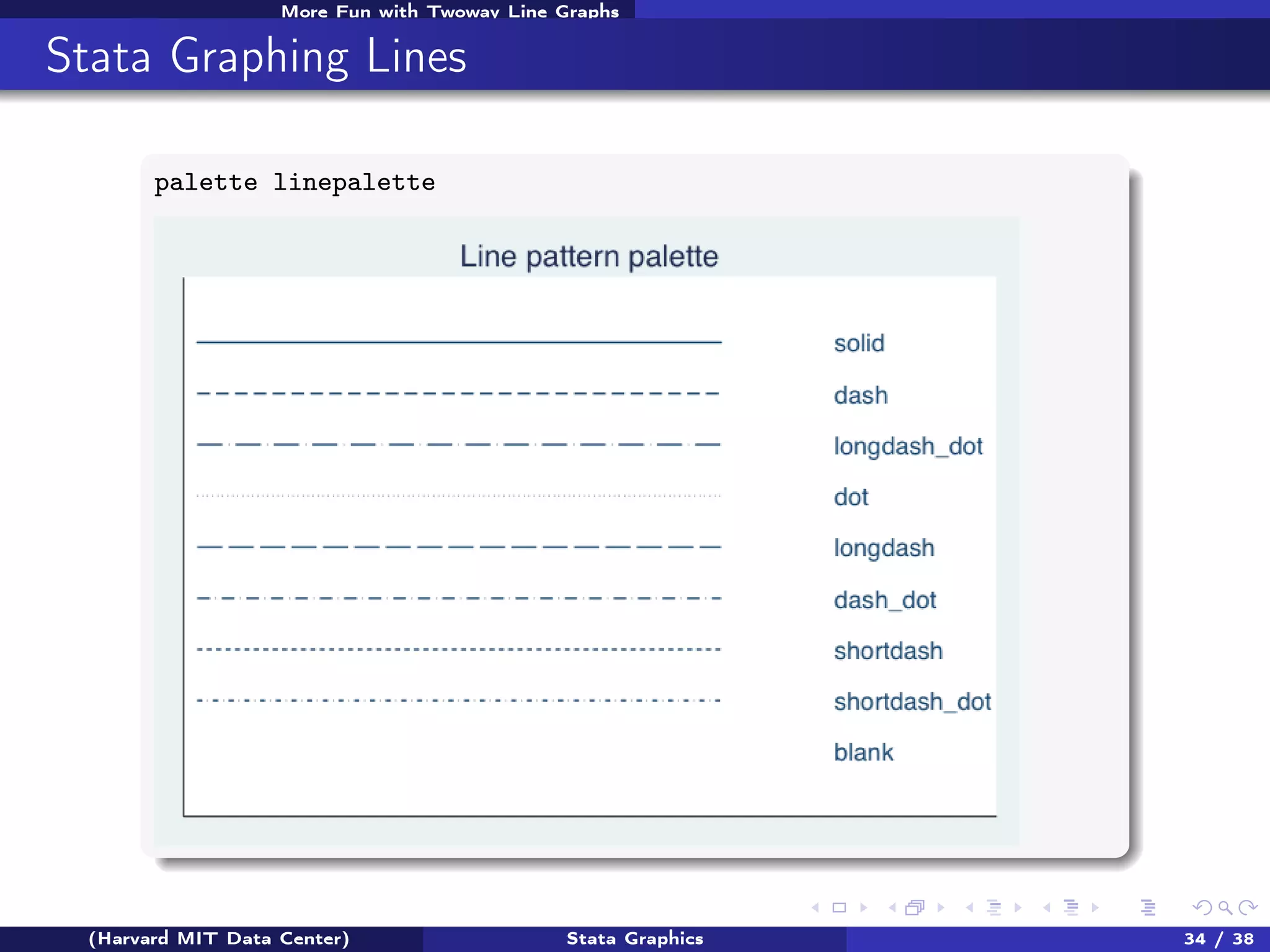
The document outlines a workshop on Stata graphics presented by the Harvard MIT Data Center, covering univariate and bivariate graphing techniques. Participants are guided through practical exercises using datasets to create histograms and twoway graphs, with an emphasis on effective graphing strategies and presentation. Additional resources and feedback information are provided to enhance future workshops.