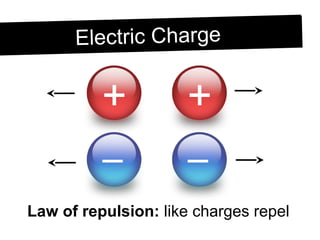
This document introduces the topics of static electricity, current electricity, and power generation. It discusses what causes static electricity, such as walking across carpet and touching something to get a shock. Static electricity occurs when electrons are not moving along a path but rather build up as they move between atoms. The document also covers electric charge, conductors, insulators, and tools for detecting electric charge like electroscopes.