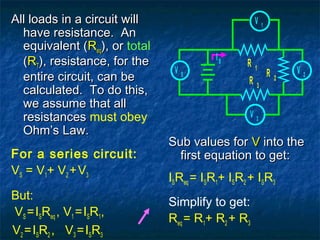
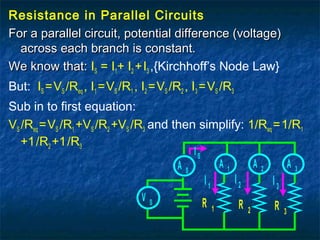
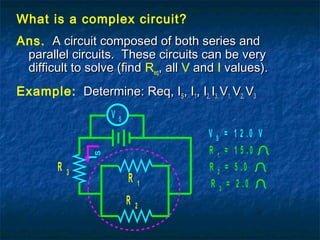
This document discusses circuits with resistance in series and parallel configurations. It explains that the total resistance (Req) of resistors in series can be calculated as the sum of the individual resistances (R1 + R2 + ... + Rn). For parallel resistors, the total resistance is calculated as the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances (1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... + 1/Rn)-1. Complex circuits contain both series and parallel components, making them more difficult to solve for total resistance and current/voltage values. An example complex circuit is worked out on the chalkboard to demonstrate the analysis process.