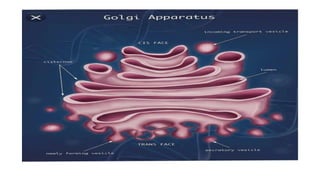
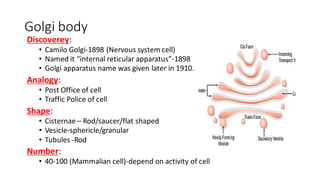
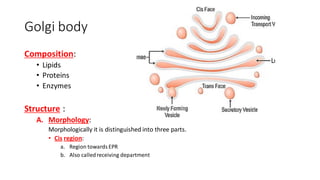
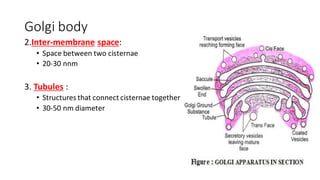
The document discusses the Golgi body (also known as the Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex), an organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It defines the Golgi body as a membrane-bound organelle made up of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae and associated vesicles. The Golgi body was discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1898. It functions to package, modify, and deliver macromolecules and is sometimes referred to as the "post office" or "traffic police" of the cell. Key components include cisternae, vesicles, and tubules that connect the cisternae. The Golgi body receives secretions from the endoplasmic reticulum and modifies and