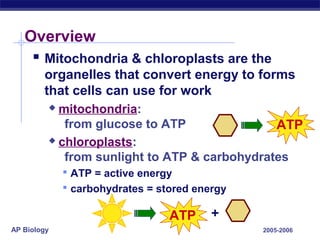
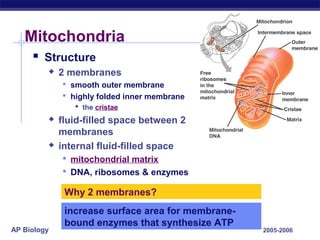
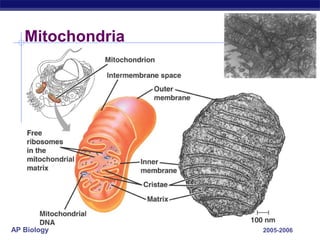
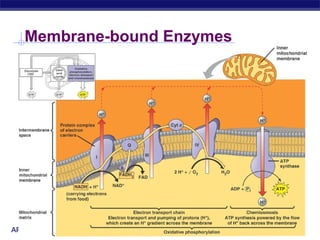
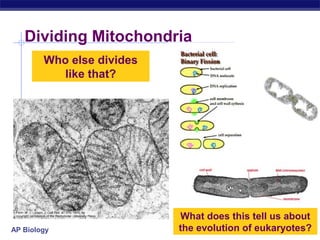
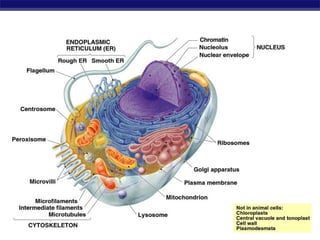
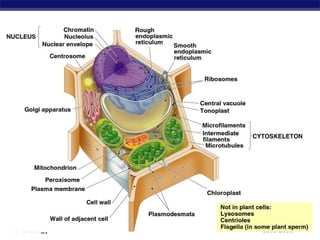
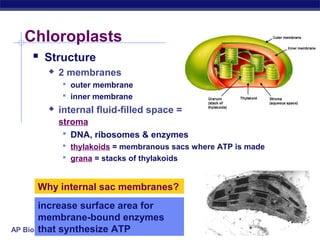
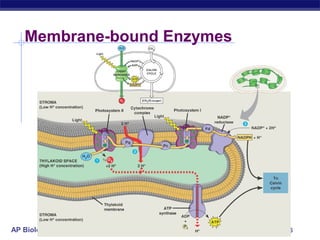
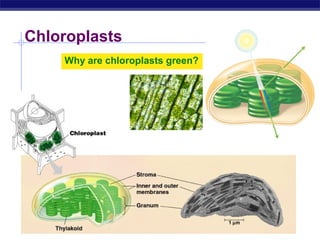
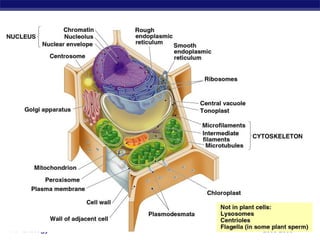
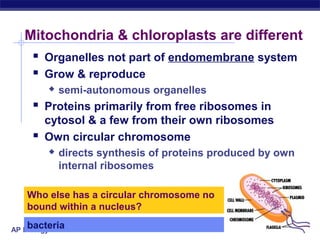
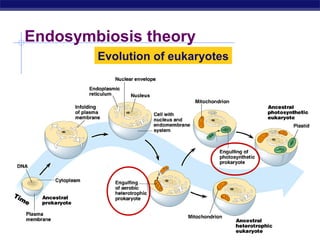
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are organelles that convert energy into forms cells can use. Mitochondria generate ATP from glucose through cellular respiration, while chloroplasts generate ATP and carbohydrates from sunlight through photosynthesis. Both organelles have double membranes, generate ATP, are semi-autonomous, and contain their own DNA, ribosomes and enzymes. Mitochondria reside in almost all eukaryotic cells and are more numerous in active cells like muscle and nerve cells. Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and algae and contain chlorophyll. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free-living bacteria that were engulfed and formed a symbiotic relationship with ancient