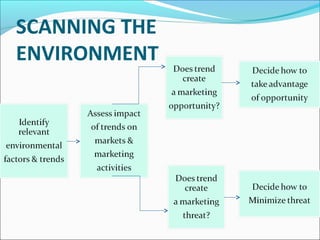
The document discusses the major elements that make up the global marketing environment: social, economic, political, legal, technological, and competitive. It states that an organization's marketing strategies and decisions depend on uncontrollable external factors in these areas. It provides examples of how changes in demographic trends, economic conditions, laws and regulations can create opportunities or threats for different markets. Finally, it emphasizes the importance of continuously scanning the external environment for influences on consumers and competition.