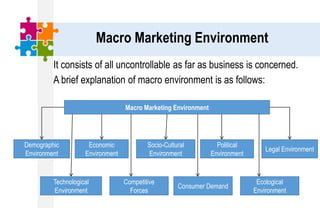
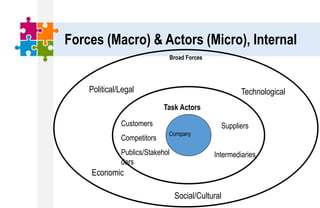
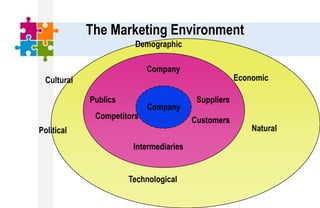
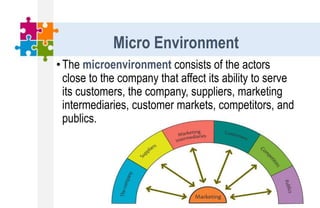
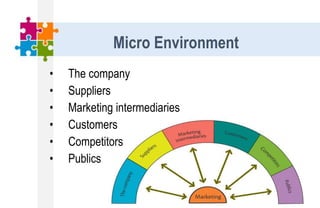
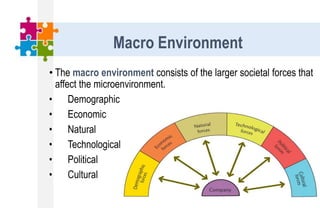
The document provides an overview of the marketing environment and its various components. It begins by defining the marketing environment and distinguishing between internal/controllable and external/uncontrollable factors. It then describes the key elements of the microenvironment including suppliers, intermediaries, customers, competitors, and publics. Finally, it outlines the macroenvironment and its demographic, economic, natural, technological, political, and cultural influences. The document aims to equip students with an understanding of the various forces that impact marketing management decisions.