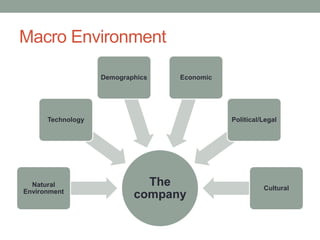
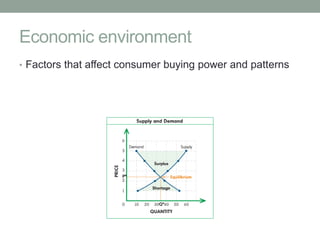
The document provides an overview of key macroenvironmental forces that shape opportunities and pose threats for companies. It discusses several components of the macroenvironment including the natural environment, technological environment, political/legal environment, economic environment, demographic environment, and cultural environment. It also covers trends related to the rise of the informal sector in South Africa such as the growth of spazas and stokvels.