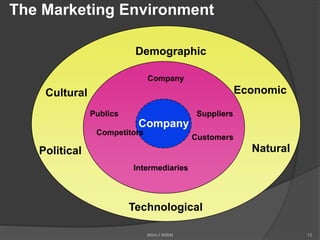
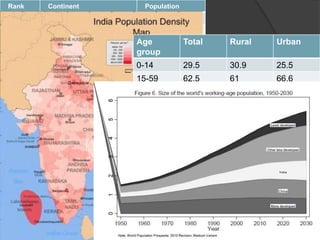
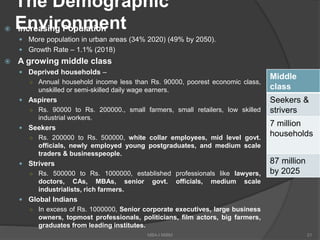
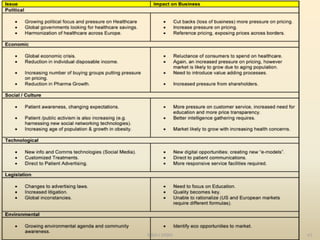
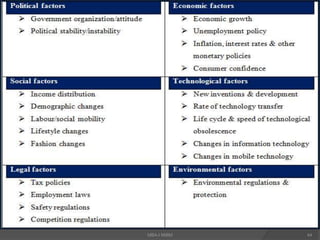
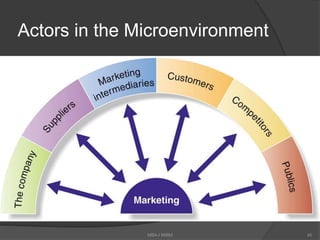
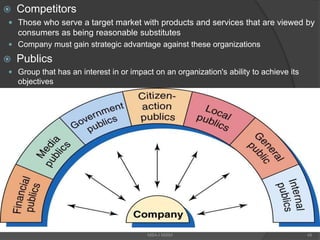
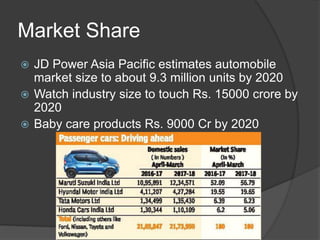
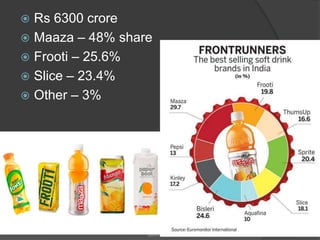
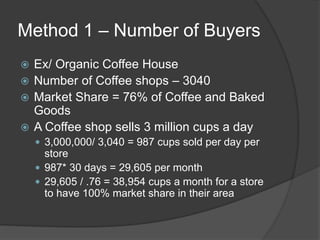
The document discusses the evolving marketing environment, highlighting factors such as technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and economic conditions that influence market dynamics. It emphasizes the importance of understanding macro and micro environments, including demographic trends and the impacts of cultural shifts on consumer behavior. Moreover, it addresses the challenges faced by market leaders and the necessity for organizations to adapt to maintain competitiveness.