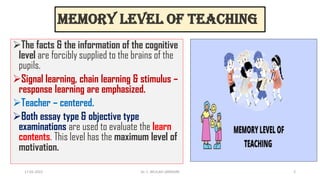
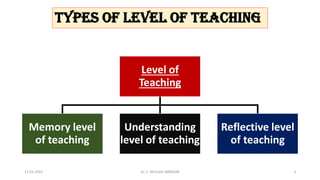
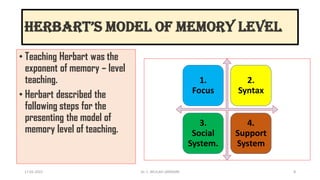
The document outlines the memory level of teaching based on the Herbartian approach developed by Johann Friedrich Herbart, which emphasizes the rote learning of facts and information through teacher-centered methods. It introduces a six-step lesson planning model that includes preparation, presentation, association, generalization, application, and recapitulation, all aimed at enhancing student retention and understanding. The approach underscores the importance of linking new knowledge with existing ideas and evaluates learning through various examination types to ensure effective teaching.