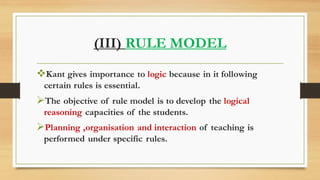
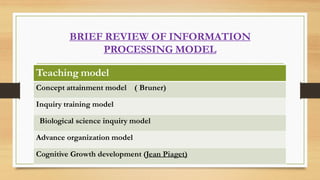
The document discusses various models of teaching that enhance teachers' skills, effectiveness, and self-evaluation capabilities. It categorizes teaching models into philosophical, psychological, and modern types, each with specific frameworks and objectives. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of these models in improving instruction quality and fostering student engagement and learning retention.