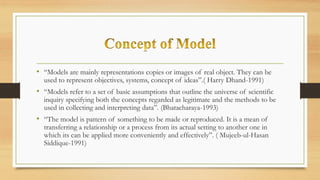
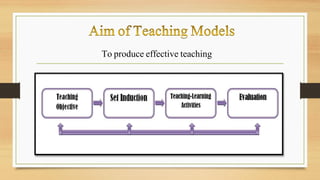
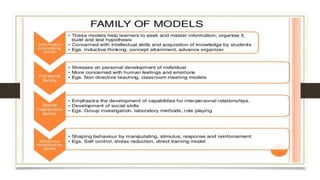
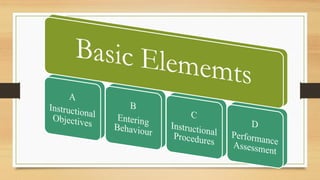
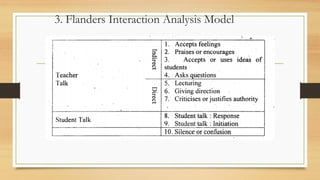
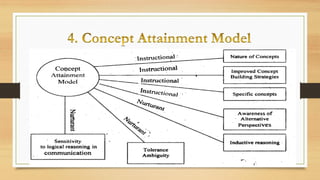
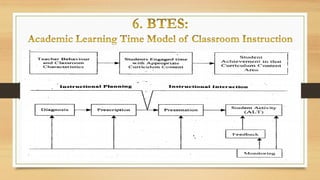
The document discusses models of teaching and their components. It states that models of teaching are plans or patterns that can be used to guide instruction and improve teaching effectiveness. The key components of models of teaching include their focus, syntax, social system, principles of reaction, and support system. Models of teaching suggest how teaching and learning conditions are interrelated and can eventually help develop empirically supported theories of teaching.